Endocrine-disrupting potential of bisphenol A, bisphenol A dimethacrylate, 4-n-nonylphenol, and 4-n-octylphenol in vitro: new data and a brief review
- PMID: 18174953
- PMCID: PMC2174402
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.9368
Endocrine-disrupting potential of bisphenol A, bisphenol A dimethacrylate, 4-n-nonylphenol, and 4-n-octylphenol in vitro: new data and a brief review
Abstract
Background: An array of environmental compounds is known to possess endocrine disruption (ED) potentials. Bisphenol A (BPA) and bisphenol A dimethacrylate (BPA-DM) are monomers used to a high extent in the plastic industry and as dental sealants. Alkylphenols such as 4-n-nonylphenol (nNP) and 4-n-octylphenol (nOP) are widely used as surfactants.
Objectives: We investigated the effect in vitro of these four compounds on four key cell mechanisms including transactivation of a) the human estrogen receptor (ER), b) the human androgen receptor (AR), c) the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), and d) aromatase activity.
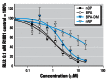
Results: All four compounds inhibited aromatase activity and were agonists and antagonists of ER and AR, respectively. nNP increased AhR activity concentration-dependently and further increased the 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin AhR action. nOP caused dual responses with a weak increased and a decreased AhR activity at lower (10(-8) M) and higher concentrations (10(-5)-10(-4) M), respectively. AhR activity was inhibited with BPA (10(-5)-10(-4) M) and weakly increased with BPA-DM (10(-5) M), respectively. nNP showed the highest relative potency (REP) compared with the respective controls in the ER, AhR, and aromatase assays, whereas similar REP was observed for the four chemicals in the AR assay.
Conclusion: Our in vitro data clearly indicate that the four industrial compounds have ED potentials and that the effects can be mediated via several cellular pathways, including the two sex steroid hormone receptors (ER and AR), aromatase activity converting testosterone to estrogen, and AhR; AhR is involved in syntheses of steroids and metabolism of steroids and xenobiotic compounds.
Keywords: BPA; BPA-DM; androgenic; aromatase; endocrine disruption; estrogenic; nNP; nOP; nuclear receptors.
Figures

References
-
- Akingbemi BT, Sottas CM, Koulova AI, Klinefelter GR, Hardy MP. Inhibition of testicular steroidogenesis by the xenoestrogen bisphenol A is associated with reduced pituitary luteinizing hormone secretion and decreased steroidogenic enzyme gene expression in rat Leydig cells. Endocrinology. 2004;145(2):592–603. - PubMed
-
- Atanassova N, McKinnell C, Turner KJ, Walker M, Fisher JS, Morley M, et al. Comparative effects of neonatal exposure of male rats to potent and weak (environmental) estrogens on spermatogenesis at puberty and the relationship to adult testis size and fertility: evidence for stimulatory effects of low estrogen levels. Endocrinology. 2000;141(10):3898–3907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
