Diagnosis of inflammatory demyelination in biopsy specimens: a practical approach
- PMID: 18175128
- PMCID: PMC2668559
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-007-0320-8
Diagnosis of inflammatory demyelination in biopsy specimens: a practical approach
Abstract
Multiple sclerosis is the most frequent demyelinating disease in adults. It is characterized by demyelination, inflammation, gliosis and a variable loss of axons. Clinically and histologically, it shares features with other demyelinating and/or inflammatory CNS diseases. Diagnosis of an inflammatory demyelinating disease can be challenging, especially in small biopsy specimens. Here, we summarize the histological hallmarks and most important neuropathological differential diagnoses of early MS, and provide practical guidelines for the diagnosis of inflammatory demyelinating diseases.
Figures
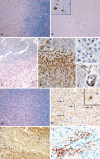

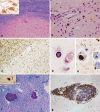

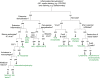
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0002-9343(52)90234-9', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(52)90234-9'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14933429', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14933429/'}]}
- Adams RD, Kubik CS (1952) The morbid anatomy of demyelinative diseases. Am J Med 12:510–546 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '13616772', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13616772/'}]}
- Adams RD, Victor M, Mancall EL (1959) Central pontine myelinolysis. A hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. Arch Neurol Psych 8138:154–172 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/1531-8249(200001)47:1<9::AID-ANA5>3.0.CO;2-I', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/1531-8249(200001)47:1<9::aid-ana5>3.0.co;2-i'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10632096', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10632096/'}]}
- Albert M, Austin L, Darnell R (2000) Detection and treatment of activated T cells in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. Ann Neurol 47:9–17 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1038/3315', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1038/3315'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9809559', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9809559/'}]}
- Albert M, Darnell J, Bender A, Francisco L, Bhardwaj N, Darnell R (1998) Tumor-specific killer cells in paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. Nat Med 4:1321–1324 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC486201', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC486201/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8558135', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8558135/'}]}
- Alderson L, Fetell MR, Sisti M, Hochberg F, Cohen M, Louis DN (1996) Sentinel lesions of primary CNS lymphoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 60:102–105 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

