The maternal plasma soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 concentration is elevated in SGA and the magnitude of the increase relates to Doppler abnormalities in the maternal and fetal circulation
- PMID: 18175242
- PMCID: PMC7062304
- DOI: 10.1080/14767050701832833
The maternal plasma soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 concentration is elevated in SGA and the magnitude of the increase relates to Doppler abnormalities in the maternal and fetal circulation
Abstract
Objectives: The soluble form of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1), an antagonist to vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor, has been implicated in the pathophysiology of preeclampsia. Preeclampsia and pregnancy complicated with small for gestational age (SGA) fetuses share some pathophysiologic derangements, such as failure of physiologic transformation of the spiral arteries, endothelial cell dysfunction, and leukocyte activation. The objectives of this study were to: (1) determine whether plasma concentrations of sVEGFR-1 in mothers with SGA fetuses without preeclampsia at the time of diagnosis are different from those in patients with preeclampsia or normal pregnant women, and (2) examine the relationship between plasma concentrations of sVEGFR-1 and Doppler velocimetry in uterine and umbilical arteries in patients with preeclampsia and those with SGA.
Study design: A cross-sectional study was conducted to determine the concentrations of the soluble form of VEGFR-1 in plasma obtained from normal pregnant women (n = 135), women with SGA fetuses (n = 53), and patients with preeclampsia (n = 112). Patients with SGA fetuses and those with preeclampsia were sub-classified according to the results of uterine and umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry examinations. Plasma concentrations of sVEGFR-1 were determined by an ELISA. Since these concentrations change with gestational age, differences among various subgroups were statistically estimated with the delta value, defined as the difference between the observed and expected plasma sVEGFR-1 concentration. The expected values were derived from regression analysis of plasma sVEGFR-1 concentrations in normal pregnancy. Regression analysis and univariate and multivariate analysis were employed.
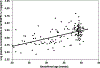
Results: (1) Mothers with SGA fetuses had a mean plasma concentration of sVEGFR-1 higher than normal pregnant women (p < 0.001), but lower than patients with preeclampsia (p < 0.001). (2) Among patients with SGA fetuses, only those with abnormal uterine artery Doppler velocimetry had a mean plasma sVEGFR-1 concentration significantly higher than normal pregnant women (p < 0.001). (3) Among mothers with SGA fetuses in whom Doppler velocimetry was performed (n = 41), those with abnormalities in both the uterine and umbilical artery velocimetry had the highest mean delta of sVEGFR-1 plasma concentration (mean +/- standard deviation (SD): 0.69 +/- 0.29). Conversely, patients who had normal Doppler velocimetry in both uterine and umbilical arteries had the lowest mean delta (mean +/- SD: 0.09 +/- 0.29) of sVEGFR-1 plasma concentrations (ANOVA; p < 0.001). (4) Among patients with preeclampsia in whom Doppler velocimetry was performed (n = 69), those with abnormalities in both the uterine and umbilical artery velocimetry had the highest mean delta sVEGFR-1 plasma concentration (mean +/- SD: 1.01 +/- 0.22) among all groups classified (ANOVA; p < 0.001). (5) Among patients with SGA and those with preeclampsia, there was a relationship (Chi-square for trend p < 0.001 for both) between the severity of Doppler velocimetry abnormalities and the proportion of patients who had high delta sVEGFR-1 plasma concentrations (defined as a concentration two standard deviations (2SD) above the mean delta of normal pregnant women). (6) Multiple regression analysis suggested that the diagnostic category (e.g., SGA or preeclampsia), Doppler abnormalities, and gestational age at blood sampling were associated with an increase in plasma sVEGFR-1 concentrations (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: These observations provide support for the participation of the soluble receptor of vascular endothelial growth factor in the pathophysiology of SGA with abnormal uterine artery Doppler velocimetry and preeclampsia. An excess of sVEGFR-1 is released into the maternal circulation of patients with preeclampsia and those with SGA fetuses, as abnormalities of impedance to blood flow involve uterine and umbilical circulation.
Figures




Comment in
-
The role of an 'anti-angiogenic state' in complications of pregnancy.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008 Jan;21(1):3-7. doi: 10.1080/14767050701855081. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008. PMID: 18175240 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A longitudinal study of angiogenic (placental growth factor) and anti-angiogenic (soluble endoglin and soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1) factors in normal pregnancy and patients destined to develop preeclampsia and deliver a small for gestational age neonate.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008 Jan;21(1):9-23. doi: 10.1080/14767050701830480. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008. PMID: 18175241 Free PMC article.
-
The use of angiogenic biomarkers in maternal blood to identify which SGA fetuses will require a preterm delivery and mothers who will develop pre-eclampsia.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29(8):1214-28. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2015.1048431. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016. PMID: 26303962 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of patients at risk for early onset and/or severe preeclampsia with the use of uterine artery Doppler velocimetry and placental growth factor.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007 Apr;196(4):326.e1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2006.11.002. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007. PMID: 17403407 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Opinion: The diagnosis and management of suspected fetal growth restriction: an evidence-based approach.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Mar;226(3):366-378. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.11.1357. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 35026129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal uterine vascular remodeling during pregnancy.Physiology (Bethesda). 2009 Feb;24:58-71. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00033.2008. Physiology (Bethesda). 2009. PMID: 19196652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A subset of patients destined to develop spontaneous preterm labor has an abnormal angiogenic/anti-angiogenic profile in maternal plasma: evidence in support of pathophysiologic heterogeneity of preterm labor derived from a longitudinal study.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009 Dec;22(12):1122-39. doi: 10.3109/14767050902994838. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009. PMID: 19916710 Free PMC article.
-
Late-onset preeclampsia is associated with an imbalance of angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors in patients with and without placental lesions consistent with maternal underperfusion.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012 May;25(5):498-507. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2011.591461. Epub 2011 Aug 25. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012. PMID: 21867402 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-eclampsia part 1: current understanding of its pathophysiology.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014 Aug;10(8):466-80. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2014.102. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 25003615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pravastatin to prevent recurrent fetal death in massive perivillous fibrin deposition of the placenta (MPFD).J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016 Mar;29(6):855-62. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2015.1022864. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016. PMID: 25893545 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profile of extracellular vesicles in maternal plasma of women with fetal death.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023 Dec;36(1):2177529. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2023.2177529. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023. PMID: 36813269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robertson WB, Brosens I, Dixon G Maternal uterine vascular lesions in the hypertensive complications of pregnancy. Perspect.Nephrol.Hypertens. 1976;5:115–127. - PubMed
-
- Brosens IA. Morphological changes in the utero-placental bed in pregnancy hypertension. Clin.Obstet Gynaecol. 1977;4:573–593. - PubMed
-
- Sheppard BL and Bonnar J An ultrastructural study of utero-placental spiral arteries in hypertensive and normotensive pregnancy and fetal growth retardation. Br.J.Obstet.Gynaecol. 1981;88:695–705. - PubMed
-
- Khong TY, De Wolf F, Robertson WB, Brosens I Inadequate maternal vascular response to placentation in pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia and by small-for-gestational age infants. Br.J Obstet Gynaecol. 1986;93:1049–1059. - PubMed
-
- Pijnenborg R, Anthony J, Davey DA, Rees A, Tiltman A, Vercruysse L, van Assche A Placental bed spiral arteries in the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1991;98:648–655. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
