Growth factor receptors and related signalling pathways as targets for novel treatment strategies of hepatocellular cancer
- PMID: 18176955
- PMCID: PMC2673371
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.1
Growth factor receptors and related signalling pathways as targets for novel treatment strategies of hepatocellular cancer
Abstract
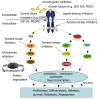
Growth factors and their corresponding receptors are commonly overexpressed and/or dysregulated in many cancers including hepatocellular cancer (HCC). Clinical trials indicate that growth factor receptors and their related signalling pathways play important roles in HCC cancer etiology and progression, thus providing rational targets for innovative cancer therapies. A number of strategies including monoclonal antibodies, tyrosine kinase inhibitors ("small molecule inhibitors") and antisense oligonucleotides have already been evaluated for their potency to inhibit the activity and downstream signalling cascades of these receptors in HCC. First clinical trials have also shown that multi-kinase inhibition is an effective novel treatment strategy in HCC. In this respect sorafenib, an inhibitor of Raf-, VEGF- and PDGF-signalling, is the first multi-kinase inhibitor that has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of advanced HCC. Moreover, the serine-threonine kinase of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) upon which the signalling of several growth factor receptors converge plays a central role in cancer cell proliferation. mTOR inhibition of HCC is currently also being studied in preclinical trials. As HCCs represent hypervascularized neoplasms, inhibition of tumour vessel formation via interfering with the VEGF/VEGFR system is another promising approach in HCC treatment. This review will summarize the current status of the various growth factor receptor-based treatment strategies and in view of the multitude of novel targeted approaches, the rationale for combination therapies for advanced HCC treatment will also be taken into account.
Figures
References
-
- Avila MA, Berasain C, Sangro B, Prieto J. New therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2006;25:3866–3884. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Davila JA, Petersen NJ, McGlynn KA. The continuing increase in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: an update. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:817–823. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P, Lindor KD. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17 Suppl:S186–S190. - PubMed
-
- McGlynn KA, Tsao L, Hsing AW, Devesa SS, Fraumeni JF Jr. International trends and patterns of primary liver cancer. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:290–296. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Hessheimer AJ, Forner A, Boix L, Vilana R, Llovet JM. New aspects of diagnosis and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2006;25:3848–3856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

