Midkine secretion protects Hep3B cells from cadmium induced cellular damage
- PMID: 18176965
- PMCID: PMC2673395
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.76
Midkine secretion protects Hep3B cells from cadmium induced cellular damage
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate role of midkine secretion during Cadmium (Cd) exposure in the human hepatocyte cell line Hep3B cells.
Methods: Different dosages of Cd (0.5-1-5-10 microg/mL) were applied to Hep3B cells and their effects to apoptosis, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) leakage and midkine secretion were evaluated as time dependent manner. Same experiments were repeated with exogenously applied midkine (250-5000 pg/mL) and/or 5 microg/mL Cd.
Results: Cd exposure induced prominent apoptosis and LDH leakage beginning from lower dosages at the 48th h. Cd induced midkine secretion with higher dosages (P < 0.001), (control, Cd 0.5-1-5-10 microg/mL respectively: 1123 +/- 73, 1157 +/- 63, 1242 +/- 90, 1886 +/- 175, 1712 +/- 166 pg/mL). Exogenous 500-5000 pg/mL midkine application during 5 microg/mL Cd toxicity prevented caspase-3 activation (control, Cd toxicity, 250, 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 pg/mL midkine+ Cd toxicity, respectively: 374 +/- 64, 1786 +/- 156, 1545 +/- 179, 1203 +/- 113, 974 +/- 116, 646 +/- 56, 556 +/- 63 cfu) LDH leakage and cell death in Hep3B cells (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Our results showed that midkine secretion from Hep3B cells during Cd exposure protects liver cells from Cd induced cellular damage. Midkine has anti-apoptotic and cytoprotective role during Cd toxicity. Further studies are needed to explain the mechanism of midkine secretion and cytoprotective role of midkine during Cd exposure. Midkine may be a promising therapeutic agent in different toxic hepatic diseases.
Figures
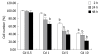

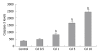

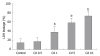

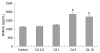
References
-
- Gubrelay U, Mehta A, Singh M, Flora SJ. Comparative hepatic and renal toxicity of cadmium in male and female rats. J Environ Biol. 2004;25:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Coutant A, Lebeau J, Bidon-Wagner N, Levalois C, Lectard B, Chevillard S. Cadmium-induced apoptosis in lymphoblastoid cell line: involvement of caspase-dependent and -independent pathways. Biochimie. 2006;88:1815–1822. - PubMed
-
- Trinchella F, Riggio M, Filosa S, Volpe MG, Parisi E, Scudiero R. Cadmium distribution and metallothionein expression in lizard tissues following acute and chronic cadmium intoxication. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006;144:272–278. - PubMed
-
- Amara S, Abdelmelek H, Garrel C, Guiraud P, Douki T, Ravanat JL, Favier A, Sakly M, Ben Rhouma K. Influence of static magnetic field on cadmium toxicity: study of oxidative stress and DNA damage in rat tissues. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2006;20:263–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

