The reticulons: a family of proteins with diverse functions
- PMID: 18177508
- PMCID: PMC2246256
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-12-234
The reticulons: a family of proteins with diverse functions
Abstract
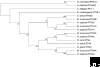
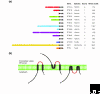
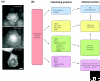
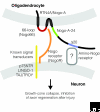
The reticulon family is a large and diverse group of membrane-associated proteins found throughout the eukaryotic kingdom. All of its members contain a carboxy-terminal reticulon homology domain that consists of two hydrophobic regions flanking a hydrophilic loop of 60-70 amino acids, but reticulon amino-terminal domains display little or no similarity to each other. Reticulons principally localize to the endoplasmic reticulum, and there is evidence that they influence endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi trafficking, vesicle formation and membrane morphogenesis. However, mammalian reticulons have also been found on the cell surface and mammalian reticulon 4 expressed on the surface of oligodendrocytes is an inhibitor of axon growth both in culture and in vivo. There is also growing evidence that reticulons may be important in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The diversity of structure, topology, localization and expression patterns of reticulons is reflected in their multiple, diverse functions in the cell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reticulons as markers of neurological diseases: focus on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Neurodegener Dis. 2005;2(3-4):185-94. doi: 10.1159/000089624. Neurodegener Dis. 2005. PMID: 16909024 Review.
-
The role of reticulons in neurodegenerative diseases.Neuromolecular Med. 2014 Mar;16(1):3-15. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8271-9. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Neuromolecular Med. 2014. PMID: 24218324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reticulon 3 is involved in membrane trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Sep 9;334(4):1198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.012. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 16054885
-
Widespread distribution of reticulon-3 in various neurodegenerative diseases.Neuropathology. 2010 Dec;30(6):574-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2010.01107.x. Neuropathology. 2010. PMID: 20374499 Free PMC article.
-
NSP-encoded reticulons, neuroendocrine proteins of a novel gene family associated with membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum.J Cell Sci. 1994 Sep;107 ( Pt 9):2403-16. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.9.2403. J Cell Sci. 1994. PMID: 7844160
Cited by
-
Nogo-B is a key mediator of hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury.Redox Biol. 2020 Oct;37:101745. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101745. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 33099216 Free PMC article.
-
RTN4B interacting protein FAM134C promotes ER membrane curvature and has a functional role in autophagy.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Jun 1;32(12):1158-1170. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-06-0409. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33826365 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Determinants of Fiber-Associated Traits in Flax Identified by Omics Data Integration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 22;23(23):14536. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314536. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36498863 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Engineering of an Iron-Resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mutant and Its Physiological and Molecular Characterization.Microorganisms. 2019 Dec 24;8(1):43. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8010043. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31878309 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic spine alterations in neocortical pyramidal neurons following postnatal neuronal Nogo-A knockdown.Dev Neurosci. 2010;32(4):313-20. doi: 10.1159/000309135. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Dev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20938157 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

