Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages
- PMID: 18177511
- PMCID: PMC2246244
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2333
Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages
Abstract
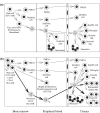
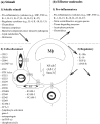
The multitude and abundance of macrophage-derived mediators in rheumatoid arthritis and their paracrine/autocrine effects identify macrophages as local and systemic amplifiers of disease. Although uncovering the etiology of rheumatoid arthritis remains the ultimate means to silence the pathogenetic process, efforts in understanding how activated macrophages influence disease have led to optimization strategies to selectively target macrophages by agents tailored to specific features of macrophage activation. This approach has two advantages: (a) striking the cell population that mediates/amplifies most of the irreversible tissue destruction and (b) sparing other cells that have no (or only marginal) effects on joint damage.
Figures

References
-
- Kinne RW, Stuhlmuller B, Palombo-Kinne E, Burmester GR. The role of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. In: Firestein GS, Panayi GS, Wollheim FA, editor. Rheumatoid Arthritis. New York: Oxford University Press; 2006. pp. 55–75.
-
- Stuhlmüller B, Ungethüm U, Scholze S, Martinez L, Backhaus M, Kraetsch HG, Kinne RW, Burmester GR. Identification of known and novel genes in activated monocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:775–790. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<775::AID-ANR8>3.0.CO;2-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maeno N, Takei S, Imanaka H, Yamamoto K, Kuriwaki K, Kawano Y, Oda H. Increased interleukin-18 expression in bone marrow of a patient with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and unrecognized macrophage-activation syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1935–1938. doi: 10.1002/art.20268. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

