Regulation of extracellular serotonin levels and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rats with high and low exploratory activity
- PMID: 18177844
- PMCID: PMC2568862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.11.041
Regulation of extracellular serotonin levels and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rats with high and low exploratory activity
Abstract
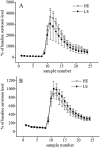
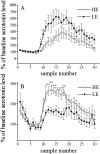
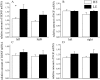
Serotonin (5-HT) system has a significant role in anxiety- and depression-related states and may be influenced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). This study examined extracellular 5-HT levels and expression of BDNF in rats with persistently low or high levels of exploratory activity (LE and HE, respectively). Baseline extracellular levels of 5-HT as assessed by in vivo microdialysis in conscious animals were similar in both groups in medial prefrontal cortex (PFC) and dentate gyrus (DG). No differences were found in parachloroamphetamine-induced 5-HT release in either region. However, LE animals had significantly higher levels of 5-HT transporter (5-HTT) binding in PFC and a larger increase in extracellular 5-HT levels after administration of citalopram (1 microM) into this area by retrograde dialysis. No difference in 5-HTT levels was found in hippocampus, while perfusion with citalopram was accompanied by a greater increase in extracellular 5-HT in the HE group in this brain region. LE-rats had higher levels of BDNF mRNA in the PFC but not hippocampus. In contrast, levels of nerve growth factor mRNA were similar in these brain regions of LE- and HE-rats. The differential regulation of 5-HT-ergic system in LE- and HE-rats in PFC and hippocampus may form the basis for their distinct anxiety-related behaviours.
Figures

References
-
- Adell A., Celada P., Artigas F. The role of 5-HT1B receptors in the regulation of serotonin cell firing and release in the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2001;79:172–182. - PubMed
-
- Altar C.A. Neurotrophins and depression. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999;20:59–61. - PubMed
-
- Alttoa A., Kõiv K., Eller M., Uustare A., Rinken A., Harro J. Effects of low dose N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine administration on exploratory and amphetamine-induced behaviour and dopamine D2 receptor function in rats with high or low exploratory activity. Neuroscience. 2005;132:979–990. - PubMed
-
- Alttoa A., Eller M., Herm L., Rinken A., Harro J. Amphetamine-induced locomotion, behavioural sensitization to amphetamine, and striatal D2 receptor function in rats with high or low spontaneous exploratory activity: differences in the role of locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 2007;1131:138–148. - PubMed
-
- Angelucci F., Mathe A.A., Aloe L. Neurotrophic factors and CNS disorders: findings in rodent models of depression and schizophrenia. Prog. Brain Res. 2004;146:151–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

