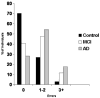
Trail Making Test errors in normal aging, mild cognitive impairment, and dementia
- PMID: 18178372
- PMCID: PMC2693196
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acn.2007.11.005
Trail Making Test errors in normal aging, mild cognitive impairment, and dementia
Abstract
The objective of the present study was to provide normative data for Trail Making Test (TMT) time to completion and performance errors among cognitively normal older adults, and to examine TMT error rates in conjunction with time scores for pre-clinical and clinical Alzheimer's disease (AD) diagnostic decision-making. A sample of 526 individuals was classified into three diagnostic groups (normal controls, N=269; mild cognitive impairment, MCI, N=200; AD, N=57) by a multidisciplinary consensus conference. Results indicated that performance differed among the three groups for TMT A and B time scores as well as TMT B error rate. Diagnostic classification accuracy (i.e., sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive powers) is described for various combinations of the diagnostic groups. The findings show that TMT B time and errors are independently meaningful scores, and both therefore have clinical utility in assessing individuals referred for dementia evaluations.
References
-
- Arbuthnott K, Frank J. Trail Making Test, Part B as a measure of executive control: Validation using a set-switching paradigm. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 2000;22:518–528. - PubMed
-
- Armitage SG. An analysis of certain psychological tests used for the evaluation of brain injury. Psychological Monographs. 1946;60:1–48.
-
- Boll TJ, Reitan RM. Effect of age on performance of the Trail Making Test. Perceptual and Motor Skills. 1973;36:691–694. - PubMed
-
- Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 1975;12:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Giovagnoli AR, Del Pesce M, Mascheroni S, Simoncelli M, Laiacona M, Capitani E. Trail Making Test: normative values from 287 normal adult controls. Italian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 1996;17:305–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical