Effect of fengycin, a lipopeptide produced by Bacillus subtilis, on model biomembranes
- PMID: 18178659
- PMCID: PMC2267117
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.114090
Effect of fengycin, a lipopeptide produced by Bacillus subtilis, on model biomembranes
Abstract
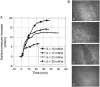
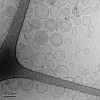
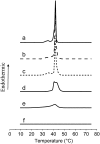
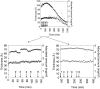
Fengycin is a biologically active lipopeptide produced by several Bacillus subtilis strains. The lipopeptide is known to develop antifungal activity against filamentous fungi and to have hemolytic activity 40-fold lower than that of surfactin, another lipopeptide produced by B. subtilis. The aim of this work is to use complementary biophysical techniques to reveal the mechanism of membrane perturbation by fengycin. These include: 1), the Langmuir trough technique in combination with Brewster angle microscopy to study the lipopeptide penetration into monolayers; 2), ellipsometry to investigate the adsorption of fengycin onto supported lipid bilayers; 3), differential scanning calorimetry to determine the thermotropic properties of lipid bilayers in the presence of fengycin; and 4), cryogenic transmission electron microscopy, which provides information on the structural organization of the lipid/lipopeptide system. From these experiments, the mechanism of fengycin action appears to be based on a two-state transition controlled by the lipopeptide concentration. One state is the monomeric, not deeply anchored and nonperturbing lipopeptide, and the other state is a buried, aggregated form, which is responsible for membrane leakage and bioactivity. The mechanism, thus, appears to be driven mainly by the physicochemical properties of the lipopeptide, i.e., its amphiphilic character and affinity for lipid bilayers.
Figures




References
-
- Vanittanakom, N., W. Loeffler, U. Koch, and G. Jung. 1986. Fengycin—a novel antifungal lipopeptide antibiotic produced by Bacillus subtilis F-29-3. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo). 39:888–901. - PubMed
-
- Jacques, P., C. Hbid, J. Destain, H. Razafindralambo, M. Paquot, E. De Pauw, and P. Thonart. 1999. Optimization of biosurfactant lipopeptide production from Bacillus subtilis S499 by Plackett-Burman design. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 77–79:223–233.
-
- Hbid, C. 1996. Contribution à l'étude de la relation entre la structure des lipopeptides de B. subtilis et leurs activités hémolytique et antifongique. PhD thesis. Université de Liège, Belgium.
-
- Schneider, J., K. Taraz, H. Budzikiewicz, M. Deleu, P. Thonart, and P. Jacques. 1999. The structure of two fengycins from Bacillus subtilis S499. Z. Naturforsch [C]. 54:859–866. - PubMed
-
- Deleu, M., M. Paquot, and T. Nylander. 2005. Fengycin interaction with lipid monolayers at the air-aqueous interface—implications for the effect of fengycin on biological membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 283:358–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

