Slowing nephropathy progression: focus on proteinuria reduction
- PMID: 18178794
- PMCID: PMC3152266
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03250807
Slowing nephropathy progression: focus on proteinuria reduction
Abstract
Blood pressure control reduces decline of kidney function. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers offer renoprotection to a small extent beyond that attributable to blood pressure lowering. These agents also reduce proteinuria, a risk marker for renal disease progression. Accumulating evidence indicates that their antiproteinuric effect correlates with their additional renal benefits.
Figures
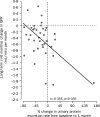


References
-
- Peterson JC, Adler S, Burkart JM, Greene T, Hebert LA, Hunsicker LG, King AJ, Klahr S, Massry SG, Seifter JL: Blood pressure control, proteinuria, and the progression of renal disease. The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study. Ann Intern Med 123 :754 –762,1995 - PubMed
-
- de Zeeuw D, Remuzzi G, Parving HH, Keane WF, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S, Snappin S, Cooper ME, Mitch WE, Brenner BM: Proteinuria, a target for renoprotection in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy: Lessons from RENAAL. Kidney Int 65 :2309 –2320,2004 - PubMed
-
- Atkins RC, Briganti EM, Lewis JB, Hunsicker LG, Braden G, Champion de Crespigny PJ, DeFerrari G, Drury P, Locatelli F, Wiegmann TB, Lewis EJ: Proteinuria reduction and progression to renal failure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and overt nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 45 :281 –287,2005 - PubMed
-
- Lea J, Greene T, Hebert L, Lipkowitz M, Massry S, Middleton J, Rostand SG, Miller E, Smith W, Bakris GL: The relationship between magnitude of proteinuria reduction and risk of end-stage renal disease: Results of the African American Study of Kidney Disease and hypertension. Arch Intern Med 165 :947 –953,2005 - PubMed
-
- Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7). National High Blood Pressure Education Program, Bethesda, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health, August2004. , NIH Publication No. 04-5230 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

