Hypokalemic nephropathy is associated with impaired angiogenesis
- PMID: 18178802
- PMCID: PMC2391040
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2007030261
Hypokalemic nephropathy is associated with impaired angiogenesis
Abstract
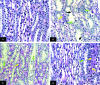
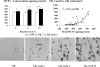
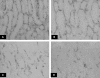
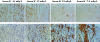
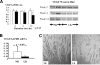
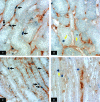
Hypokalemic nephropathy is associated with alterations in intrarenal vasoactive substances, leading to vasoconstriction, salt-sensitivity, and progression of interstitial fibrosis. In this study, we investigated whether hypokalemic nephropathy might also involve impaired renal angiogenesis. Sprague-Dawley rats that were fed low-potassium diets developed peritubular capillary loss that began in the inner stripe of the outer medulla (week 2) and progressed to the outer stripe of the outer medulla (week 4) and cortex (week 12). These changes were associated with increased macrophage infiltration, increased expression of both monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and TNF-alpha, and a loss of vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Renal thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances, markers of oxidative stress, were increased late in disease. In conclusion, hypokalemic nephropathy is associated with impaired renal angiogenesis, evidenced by progressive capillary loss, reduced endothelial cell proliferation, and loss of VEGF expression.
Figures


References
-
- Amlal H, Krane CM, Chen Q, Soleimani M: Early polyuria and urinary concentrating defect in potassium deprivation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279: F655–F663, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Kimura T, Nishino T, Maruyama N, Hamano K, Kubo A, Iwano M, Shiiki H: Expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in hypokalemic nephropathy in rats. Pathobiology 69: 237–248, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Tsao T, Fawcett J, Fervenza FC, Hsu FW, Huie P, Sibley RK, Rabkin R: Expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 and transforming growth factor-beta in hypokalemic nephropathy in the rat. Kidney Int 59: 96–105, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

