Haloperidol and clozapine differentially affect the expression of arrestins, receptor kinases, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation
- PMID: 18178904
- PMCID: PMC2629350
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.107.131987
Haloperidol and clozapine differentially affect the expression of arrestins, receptor kinases, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation
Abstract
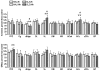
Dopamine and other G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent the major target of antipsychotic drugs. GPCRs undergo desensitization via activation-dependent phosphorylation by G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) followed by arrestin binding. Arrestins and GRKs are major regulators of GPCR signaling. We elucidated changes in expression of two arrestins and four GRKs following chronic (21 days) treatment with haloperidol (1 mg/kg i.p.) or clozapine (20 mg/kg i.p.) 2 or 24 h after the last injection in 11 brain regions. Haloperidol decreased GRK3 in ventrolateral caudate-putamen and transiently down-regulated GRK5 in globus pallidus and caudal caudate-putamen. Clozapine also caused a short-term suppression of the GRK5 expression in the caudal caudate-putamen and globus pallidus, but, unlike haloperidol, elevated GRK5 in the caudal caudate-putamen after 24 h. Unlike haloperidol, clozapine decreased arrestin2 and GRK3 in hippocampus and GRK3 in globus pallidus but increased arrestin2 in the core of nucleus accumbens and ventrolateral caudate-putamen and GRK2 in prefrontal cortex. Clozapine, but not haloperidol, induced long-term activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 2 in ventrolateral caudate-putamen and transient in prefrontal cortex. The data demonstrate that haloperidol and clozapine differentially affect the expression of arrestins and GRKs and ERK activity, which may play a role in determining their clinical profile.
Figures
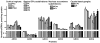
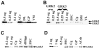

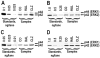

References
-
- Abi-Dargham A, Laruelle M. Mechanisms of action of second generation antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: insights from brain imaging studies. Eur Psychiatry. 2005;20:15–27. - PubMed
-
- Alimohamad H, Rajakumar N, Seah YH, Rushlow W. Antipsychotics alter the protein expression levels of beta-catenin and GSK-3 in the rat medial prefrontal cortex and striatum. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57:533–542. - PubMed
-
- Baldessarini RJ, Centorrino F, Flood JG, Volpicelli SA, Huston-Lyons D, Cohen BM. Tissue concentrations of clozapine and its metabolites in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1993;9:117–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM63097/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059802/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM47417/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM044944/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM44944/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- EY11500/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062654/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS045117/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045117/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM063097/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 MH062651/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM59802/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM047417/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY011500/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- MH62654/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM047417/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

