Risk of female human papillomavirus acquisition associated with first male sex partner
- PMID: 18179386
- PMCID: PMC2875685
- DOI: 10.1086/524875
Risk of female human papillomavirus acquisition associated with first male sex partner
Abstract
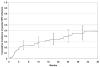
To quantify the risk of human papillomavirus (HPV) acquisition associated with a first male sex partner and to identify associated risk factors, we analyzed data from women who were enrolled before or within 3 months of first intercourse with a male partner and were censored at the report of a second partner. The 1-year cumulative incidence of first HPV infection was 28.5% (95% confidence interval, 20.6%-38.6%) and increased to almost 50% by 3 years. The risk was increased when the first male partner was sexually experienced. Our results indicate a high risk of HPV infection in young women who have had just 1 male sex partner.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: none reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Young women's risk for first HPV infection was high and increased when the first male partner was sexually experienced.ACP J Club. 2008 Jul;149(1):14. ACP J Club. 2008. PMID: 18624382 No abstract available.
-
Young women's risk of first HPV infection was high and increased when the first male partner was sexually experienced.Evid Based Med. 2008 Aug;13(4):121. doi: 10.1136/ebm.13.4.121. Evid Based Med. 2008. PMID: 18667680 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ho GYF, Bierman R, Beardsley L, Chang CJ, Burk RD. Natural history of cervicovaginal papillomavirus infection in young women. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:423–8. - PubMed
-
- Winer RL, Lee SK, Hughes JP, Adam DE, Kiviat NB, Koutsky LA. Incident infection with genital human papillomavirus: rates and risk factors among a cohort of female university students. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;157:218–26. - PubMed
-
- Woodman CB, Collins S, Winter H, et al. Natural history of cervical human papillomavirus infection in young women: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet. 2001;357:1831–6. - PubMed
-
- Winer RL, Hughes JP, Feng Q, et al. Condom use and the risk of genital human papillomavirus infection in young women. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2645–54. - PubMed
-
- Burchell AN, Winer RL, de Sanjosé S, Franco EL. Chapter 6: epidemiology and transmission dynamics of genital HPV infection. Vaccine. 2006;24(Suppl 3):S52–61. - PubMed