The Bacillus subtilis sigma(M) regulon and its contribution to cell envelope stress responses
- PMID: 18179421
- PMCID: PMC3025603
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06090.x
The Bacillus subtilis sigma(M) regulon and its contribution to cell envelope stress responses
Abstract
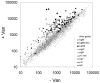
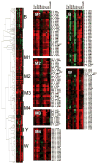
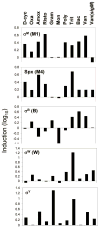
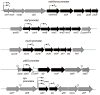
The Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma(M) factor is activated by cell envelope stress elicited by antibiotics, and by acid, heat, ethanol and superoxide stresses. Here, we have used several complementary approaches to identify genes controlled by sigma(M). In many cases, expression is only partially dependent on sigma(M) because of both overlapping promoter recognition with other ECF sigma factors and the presence of additional promoter elements. Genes regulated by sigma(M) have a characteristic pattern of induction in response to cell envelope-acting antibiotics as evidenced by hierarchical clustering analysis. sigma(M) also contributes to the expression of the Spx transcription factor and thereby indirectly regulates genes of the Spx regulon. Cell envelope stress responses also include regulons controlled by sigma(W), sigma(B) and several two-component regulatory systems (e.g. LiaRS, YycFG, BceRS). Activation of the sigma(M) regulon increases expression of proteins functioning in transcriptional control, cell wall synthesis and shape determination, cell division, DNA damage monitoring, recombinational repair and detoxification.
Figures

References
-
- Alba BM, Gross CA. Regulation of the Escherichia coliσE-dependent envelope stress response. Mol Microbiol. 2004;52:613–619. - PubMed
-
- Asai K, Yamaguchi H, Kang CM, Yoshida K, Fujita Y, Sadaie Y. DNA microarray analysis of Bacillus subtilis sigma factors of extracytoplasmic function family. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003;220:155–160. - PubMed
-
- Bauer R, Dicks LM. Mode of action of lipid II-targeting lantibiotics. Int J Food Microbiol. 2005;101:201–216. - PubMed
-
- Bejerano-Sagie M, Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y, Berlatzky I, Rouvinski A, Meyerovich M, Ben-Yehuda S. A checkpoint protein that scans the chromosome for damage at the start of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Cell. 2006;125:679–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

