Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: a link between inflammation and neurodegeneration
- PMID: 18180036
- PMCID: PMC2895566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.10.007
Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: a link between inflammation and neurodegeneration
Abstract
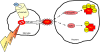
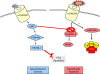
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the leading cause of dementia affecting over 25 million people worldwide. Classical studies focused on the description and characterization of the pathological hallmarks found in AD patients including the neurofibrillary tangles and the amyloid plaques. Current strategies focus on the etiology of these hallmarks and the different mechanisms contributing to neurodegeneration. Among them, recent studies reveal the close interplay between the immunological and the neurodegenerative processes. This article examines the implications of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (alpha7nAChR) as a critical link between inflammation and neurodegeneration in AD. Alpha7nAChRs are not only expressed in neurons but also in Glia cells where they can modulate the immunological responses contributing to AD. Successful therapeutic strategies against AD should consider the connections between inflammation and neurodegeneration. Among them, alpha7nAChR may represent a pharmacological target to control these two mechanisms during the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative and behavioral disorders.
Figures


References
-
- Adler LE, Hoffer LD, Wiser A, Freedman R. Normalization of auditory physiology by cigarette smoking in schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry. 1993;150:1856–1861. - PubMed
-
- Adler LE, Olincy A, Waldo M, Harris JG, Griffith J, Stevens K, Flach K, Nagamoto H, Bickford P, Leonard S, Freedman R. Schizophrenia, sensory gating, and nicotinic receptors. Schizophrenia Bulletin. 1998;24:189–202. - PubMed
-
- Aisen PS, Davis KL, Berg JD, Schafer K, Campbell K, Thomas RG, Weiner MF, Farlow MR, Sano M, Grundman M, Thal LJ. A randomized controlled trial of prednisone in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study [see comment] Neurology. 2000;54:588–593. - PubMed
-
- Aisen PS, Schafer KA, Grundman M, Pfeiffer E, Sano M, Davis KL, Farlow MR, Jin S, Thomas RG, Thal LJ, Study., A.S.D.C. Effects of rofecoxib or naproxen vs placebo on Alzheimer disease progression: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2003;289:2819–2826. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama H, Arai T, Kondo H, Tanno E, Haga C, Ikeda K. Cell mediators of inflammation in the Alzheimer disease brain. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders. 2000;14(Suppl. 1):S47–S53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

