Improved genome-wide localization by ChIP-chip using double-round T7 RNA polymerase-based amplification
- PMID: 18180247
- PMCID: PMC2275083
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm1144
Improved genome-wide localization by ChIP-chip using double-round T7 RNA polymerase-based amplification
Abstract
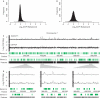
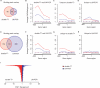
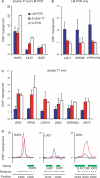
Chromatin immunoprecipitation combined with DNA microarrays (ChIP-chip) is a powerful technique to detect in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Due to low yields, ChIP assays of transcription factors generally require amplification of immunoprecipitated genomic DNA. Here, we present an adapted linear amplification method that involves two rounds of T7 RNA polymerase amplification (double-T7). Using this we could successfully amplify as little as 0.4 ng of ChIP DNA to sufficient amounts for microarray analysis. In addition, we compared the double-T7 method to the ligation-mediated polymerase chain reaction (LM-PCR) method in a ChIP-chip of the yeast transcription factor Gsm1p. The double-T7 protocol showed lower noise levels and stronger binding signals compared to LM-PCR. Both LM-PCR and double-T7 identified strongly bound genomic regions, but the double-T7 method increased sensitivity and specificity to allow detection of weaker binding sites.
Figures


References
-
- Yuan GC, Liu YJ, Dion MF, Slack MD, Wu LF, Altschuler SJ, Rando OJ. Genome-scale identification of nucleosome positions in S. cerevisiae. Science. 2005;309:626–630. - PubMed
-
- Pokholok DK, Harbison CT, Levine S, Cole M, Hannett NM, Lee TI, Bell GW, Walker K, Rolfe PA, Herbolsheimer E, et al. Genome-wide map of nucleosome acetylation and methylation in yeast. Cell. 2005;122:517–527. - PubMed
-
- Hecht A, Strahl-Bolsinger S, Grunstein M. Mapping DNA interaction sites of chromosomal proteins. Crosslinking studies in yeast. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999;119:469–479. - PubMed
-
- Strutt H, Paro R. Mapping DNA target sites of chromatin proteins in vivo by formaldehyde crosslinking. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999;119:455–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

