Mannose-binding lectin enhances Toll-like receptors 2 and 6 signaling from the phagosome
- PMID: 18180310
- PMCID: PMC2234382
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20071164
Mannose-binding lectin enhances Toll-like receptors 2 and 6 signaling from the phagosome
Abstract
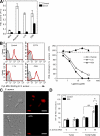
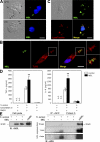
Innate immunity is the first-line defense against pathogens and relies on phagocytes, soluble components, and cell-surface and cytosolic pattern recognition receptors. Despite using hard-wired receptors and signaling pathways, the innate immune response demonstrates surprising specificity to different pathogens. We determined how combinatorial use of innate immune defense mechanisms defines the response. We describe a novel cooperation between a soluble component of the innate immune system, the mannose-binding lectin, and Toll-like receptor 2 that both specifies and amplifies the host response to Staphylococcus aureus. Furthermore, we demonstrate that this cooperation occurs within the phagosome, emphasizing the importance of engulfment in providing the appropriate cellular environment to facilitate the synergy between these defense pathways.
Figures
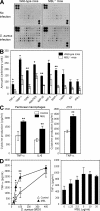
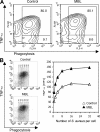
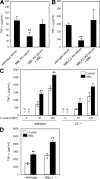
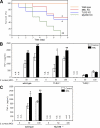
References
-
- Hoffmann, J.A., F.C. Kafatos, C.A. Janeway, and R.A. Ezekowitz. 1999. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science. 284:1313–1318. - PubMed
-
- Janeway, C.A., Jr. 1989. Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 54:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Janeway, C.A., Jr., and R. Medzhitov. 2002. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S., and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Underhill, D.M., and A. Ozinsky. 2002. Phagocytosis of microbes: complexity in action. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20:825–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

