Semaphorin 3A suppresses VEGF-mediated angiogenesis yet acts as a vascular permeability factor
- PMID: 18180379
- PMCID: PMC2254547
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-08-110205
Semaphorin 3A suppresses VEGF-mediated angiogenesis yet acts as a vascular permeability factor
Abstract
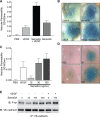
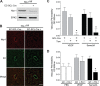
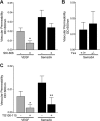
Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A), a known inhibitor of axonal sprouting, also alters vascular patterning. Here we show that Sema3A selectively interferes with VEGF- but not bFGF-induced angiogenesis in vivo. Consistent with this, Sema3A disrupted VEGF- but not bFGF-mediated endothelial cell signaling to FAK and Src, key mediators of integrin and growth factor signaling; however, signaling to ERK by either growth factor was unperturbed. Since VEGF is also a vascular permeability (VP) factor, we examined the role of Sema3A on VEGF-mediated VP in mice. Surprisingly, Sema3A not only stimulated VEGF-mediated VP but also potently induced VP in the absence of VEGF. Sema3A-mediated VP was inhibited either in adult mice expressing a conditional deletion of endothelial neuropilin-1 (Nrp-1) or in wild-type mice systemically treated with a function-blocking Nrp-1 antibody. While both Sema3A- and VEGF-induced VP was Nrp-1 dependent, they use distinct downstream effectors since VEGF- but not Sema3A-induced VP required Src kinase signaling. These findings define a novel role for Sema3A both as a selective inhibitor of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis and a potent inducer of VP.
Figures

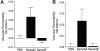
References
-
- Yazdani U, Terman JR. The semaphorins. Genome Biol. 2006 7:211. [Accessed May 23, 2006]; ( http://genomebiology.com) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Serini G, Valdembri D, Zanivan S, et al. Class 3 semaphorins control vascular morphogenesis by inhibiting integrin function. Nature. 2003;424:391–397. - PubMed
-
- Shoji W, Isogai S, Sato-Maeda M, Obinata M, Kuwada JY. Semaphorin3a1 regulates angioblast migration and vascular development in zebrafish embryos. Development. 2003;130:3227–3236. - PubMed
-
- Torres-Vazquez J, Gitler AD, Fraser SD, et al. Semaphorin-plexin signaling guides patterning of the developing vasculature. Dev Cell. 2004;7:117–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

