Dynamitin mutagenesis reveals protein-protein interactions important for dynactin structure
- PMID: 18182012
- PMCID: PMC4157825
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00702.x
Dynamitin mutagenesis reveals protein-protein interactions important for dynactin structure
Abstract
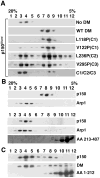
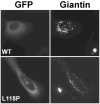
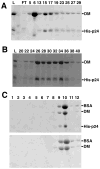
Dynactin is a highly conserved, multiprotein complex that works in conjunction with microtubule-based motors to power a variety of intracellular motile events. Dynamitin (p50) is a core element of dynactin structure. In the present study, we use targeted mutagenesis to evaluate how dynamitin's different structural domains contribute to its ability to self-associate, interact with dynactin and assemble into a complex with its close binding partner, p24. We show that these interactions involve three distinct structural elements: (i) a previously unidentified dimerization motif in the N-terminal 100 amino acids, (ii) an alpha-helical motif spanning aa 106-162 and (iii) the C-terminal half of the molecule (aa 213-406), which is predicted to fold into an antiparallel alpha-helix bundle. The N-terminal half of dynamitin by itself is sufficient to disrupt dynactin, although very high concentrations are required. The ability of mutations in dynamitin's interaction domains to disrupt dynactin in vitro was found to correlate with their inhibitory effects when expressed in cells. We determined that the dynactin subunit, p24, governs dynamitin oligomerization by binding dynamitin along its length. This suppresses aberrant multimerization and drives formation of a protein complex that is identical to the native dynactin shoulder.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dynactin integrity depends upon direct binding of dynamitin to Arp1.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Jul 15;25(14):2171-80. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-03-0842. Epub 2014 May 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24829381 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and functional basis for the scaffolding role of the p50/dynamitin subunit of the microtubule-associated dynactin complex.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 23;285(30):23019-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.100602. Epub 2010 May 12. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20463029 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of dynamitin-mediated disruption of dynactin.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jul 6;282(27):19355-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700003200. Epub 2007 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17449914
-
The role of the dynactin complex in intracellular motility.Int Rev Cytol. 1998;182:69-109. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62168-3. Int Rev Cytol. 1998. PMID: 9522459 Review.
-
Dynactin.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:759-79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.20.012103.094623. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15473859 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynein mediates the localization and activation of mTOR in normal and human cytomegalovirus-infected cells.Genes Dev. 2012 Sep 15;26(18):2015-26. doi: 10.1101/gad.196147.112. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22987636 Free PMC article.
-
Dynactin integrity depends upon direct binding of dynamitin to Arp1.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Jul 15;25(14):2171-80. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-03-0842. Epub 2014 May 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24829381 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the eukaryotic dynactin complex, the activator of cytoplasmic dynein.BMC Evol Biol. 2012 Jun 22;12:95. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-12-95. BMC Evol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22726940 Free PMC article.
-
VezA/vezatin facilitates proper assembly of the dynactin complex in vivo.Cell Rep. 2024 Nov 26;43(11):114943. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114943. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39487986 Free PMC article.
-
Dynein and dynactin leverage their bivalent character to form a high-affinity interaction.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e59453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059453. Epub 2013 Apr 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23577064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melkonian KA, Maier KC, Godfrey JE, Rodgers M, Schroer TA. Mechanism of dynamitin-mediated disruption of dynactin. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:19355–19364. - PubMed
-
- Imai H, Narita A, Schroer TA, Maeda Y. Two-dimensional averaged images of the dynactin complex revealed by single particle analysis. J Mol Biol. 2006;359:833–839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

