The itinerary of autophagosomes: from peripheral formation to kiss-and-run fusion with lysosomes
- PMID: 18182013
- PMCID: PMC2329914
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00701.x
The itinerary of autophagosomes: from peripheral formation to kiss-and-run fusion with lysosomes
Abstract
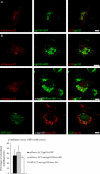
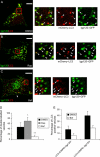
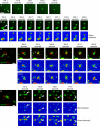
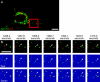
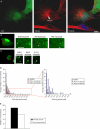
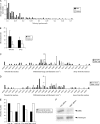
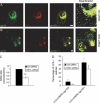
Macroautophagy, a constitutive process in higher eukaryotic cells, mediates degradation of many long-lived proteins and organelles. The actual events occurring during the process in the dynamic system of a living cell have never been thoroughly investigated. We aimed to develop a live-cell assay in which to follow the complete itinerary of an autophagosome. Our experiments show that autophagosomes are formed randomly in peripheral regions of the cell. They then move bidirectionally along microtubules, accumulating at the microtubule-organizing centre, in a similar way to lysosomes. Their centripetal movement is dependent on the motor protein dynein and is important for their fusion with lysosomes. Initially, autophagosomes dock on to lysosomes, independent of lysosomal acidification. Two kinds of fusion then occur: complete fusions, creating a hybrid organelle, or more often kiss-and-run fusions, i.e. transfer of some content while still maintaining two separate vesicles. Surprisingly, the autophagolysosomal compartment seems to be more long lived than expected. Our study documents many aspects of autophagosome behaviour, adding to our understanding of the mechanism and control of autophagy. Indeed, although the formation of autophagosomes is completely different from any other vesicular structures, their later itinerary appears to be very similar to those of other trafficking pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Rubinsztein DC, Gestwicki JE, Murphy LO, Klionsky DJ. Potential therapeutic applications of autophagy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:304–312. - PubMed
-
- Kimura S, Noda T, Yoshimori T. Dissection of the autophagosome maturation process by a novel reporter protein, tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3. Autophagy. 2007;3:452–460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

