High field gradient targeting of magnetic nanoparticle-loaded endothelial cells to the surfaces of steel stents
- PMID: 18182491
- PMCID: PMC2206599
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0708338105
High field gradient targeting of magnetic nanoparticle-loaded endothelial cells to the surfaces of steel stents
Abstract
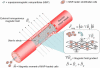
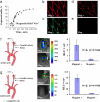
A cell delivery strategy was investigated that was hypothesized to enable magnetic targeting of endothelial cells to the steel surfaces of intraarterial stents because of the following mechanisms: (i) preloading cells with biodegradable polymeric superparamagnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), thereby rendering the cells magnetically responsive; and (ii) the induction of both magnetic field gradients around the wires of a steel stent and magnetic moments within MNPs because of a uniform external magnetic field, thereby targeting MNP-laden cells to the stent wires. In vitro studies demonstrated that MNP-loaded bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) could be magnetically targeted to steel stent wires. In vivo MNP-loaded BAECs transduced with adenoviruses expressing luciferase (Luc) were targeted to stents deployed in rat carotid arteries in the presence of a uniform magnetic field with significantly greater Luc expression, detected by in vivo optical imaging, than nonmagnetic controls.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting stents with local delivery of paclitaxel-loaded magnetic nanoparticles using uniform fields.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 4;107(18):8346-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909506107. Epub 2010 Apr 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20404175 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetically responsive paclitaxel-loaded biodegradable nanoparticles for treatment of vascular disease: preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation of anti-proliferative potential.Curr Drug Deliv. 2010 Oct;7(4):263-73. doi: 10.2174/156720110793360621. Curr Drug Deliv. 2010. PMID: 20695837
-
Functional behavior and gene expression of magnetic nanoparticle-loaded primary endothelial cells for targeting vascular stents.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015 May;10(9):1391-406. doi: 10.2217/nnm.15.13. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25996117 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetically modulated nanosystems: a unique drug-delivery platform.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2009 Oct;4(7):799-812. doi: 10.2217/nnm.09.66. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2009. PMID: 19839815 Review.
-
Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Mar 8;62(3):284-304. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.11.002. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010. PMID: 19909778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Helios as a Potential Biomarker in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and New Therapies Based on Immunosuppressive Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):452. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010452. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous steering and imaging of magnetic particles using MRI toward delivery of therapeutics.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 26;6:33567. doi: 10.1038/srep33567. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27666666 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Uncoated SPIONs on hiPSC-Differentiated Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 19;20(14):3536. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143536. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31331030 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic targeting enhances retrograde cell retention in a rat model of myocardial infarction.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(6):149. doi: 10.1186/scrt360. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24330751 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomagnetic activation as a way to control the efficacy of nucleic acid delivery.Pharm Res. 2015 Jan;32(1):103-21. doi: 10.1007/s11095-014-1448-6. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 25033763
References
-
- Varenne O, Pislaru S, Gillijns H, Van Pelt N, Gerard RD, Zoldhelyi P, Van de Werf F, Collen D, Janssens SP. Circulation. 1998;98:919–926. - PubMed
-
- Gulati R, Jevremovic D, Peterson TE, Witt TA, Kleppe LS, Mueske CS, Lerman A, Vile RG, Simari RD. Circulation. 2003;108:1520–1526. - PubMed
-
- Fattori R, Piva T. Lancet. 2003;361:247–249. - PubMed
-
- Kipshidze NN, Tsapenko MV, Leon MB, Stone GW, Moses JW. Exp Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2005;3:953–968. - PubMed
-
- Burt HM, Hunter WL. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58:350–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

