High field gradient targeting of magnetic nanoparticle-loaded endothelial cells to the surfaces of steel stents
- PMID: 18182491
- PMCID: PMC2206599
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0708338105
High field gradient targeting of magnetic nanoparticle-loaded endothelial cells to the surfaces of steel stents
Abstract
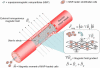
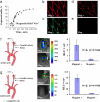
A cell delivery strategy was investigated that was hypothesized to enable magnetic targeting of endothelial cells to the steel surfaces of intraarterial stents because of the following mechanisms: (i) preloading cells with biodegradable polymeric superparamagnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), thereby rendering the cells magnetically responsive; and (ii) the induction of both magnetic field gradients around the wires of a steel stent and magnetic moments within MNPs because of a uniform external magnetic field, thereby targeting MNP-laden cells to the stent wires. In vitro studies demonstrated that MNP-loaded bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) could be magnetically targeted to steel stent wires. In vivo MNP-loaded BAECs transduced with adenoviruses expressing luciferase (Luc) were targeted to stents deployed in rat carotid arteries in the presence of a uniform magnetic field with significantly greater Luc expression, detected by in vivo optical imaging, than nonmagnetic controls.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Varenne O, Pislaru S, Gillijns H, Van Pelt N, Gerard RD, Zoldhelyi P, Van de Werf F, Collen D, Janssens SP. Circulation. 1998;98:919–926. - PubMed
-
- Gulati R, Jevremovic D, Peterson TE, Witt TA, Kleppe LS, Mueske CS, Lerman A, Vile RG, Simari RD. Circulation. 2003;108:1520–1526. - PubMed
-
- Fattori R, Piva T. Lancet. 2003;361:247–249. - PubMed
-
- Kipshidze NN, Tsapenko MV, Leon MB, Stone GW, Moses JW. Exp Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2005;3:953–968. - PubMed
-
- Burt HM, Hunter WL. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58:350–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

