Vascular disrupting action of electroporation and electrochemotherapy with bleomycin in murine sarcoma
- PMID: 18182988
- PMCID: PMC2361464
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604168
Vascular disrupting action of electroporation and electrochemotherapy with bleomycin in murine sarcoma
Abstract
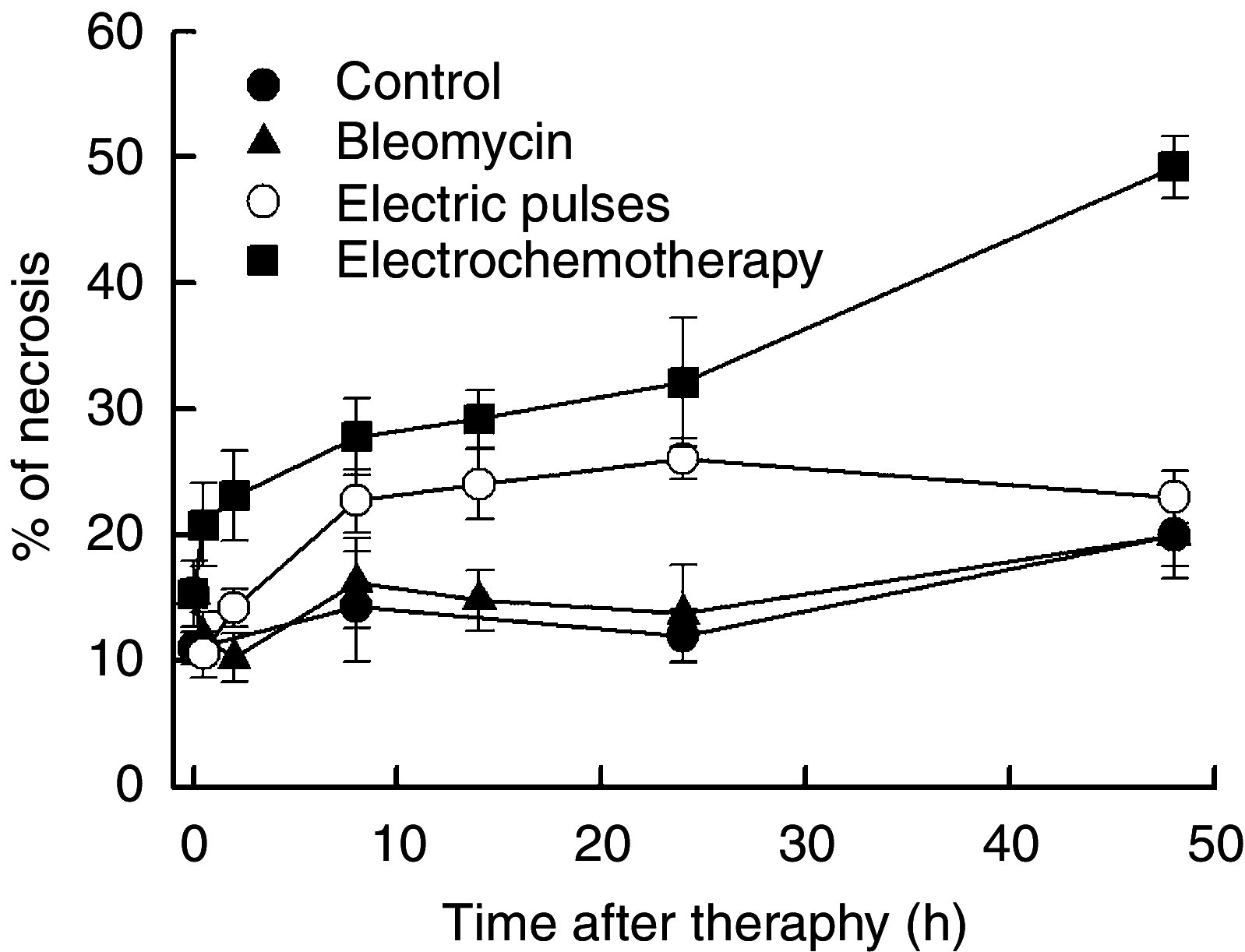
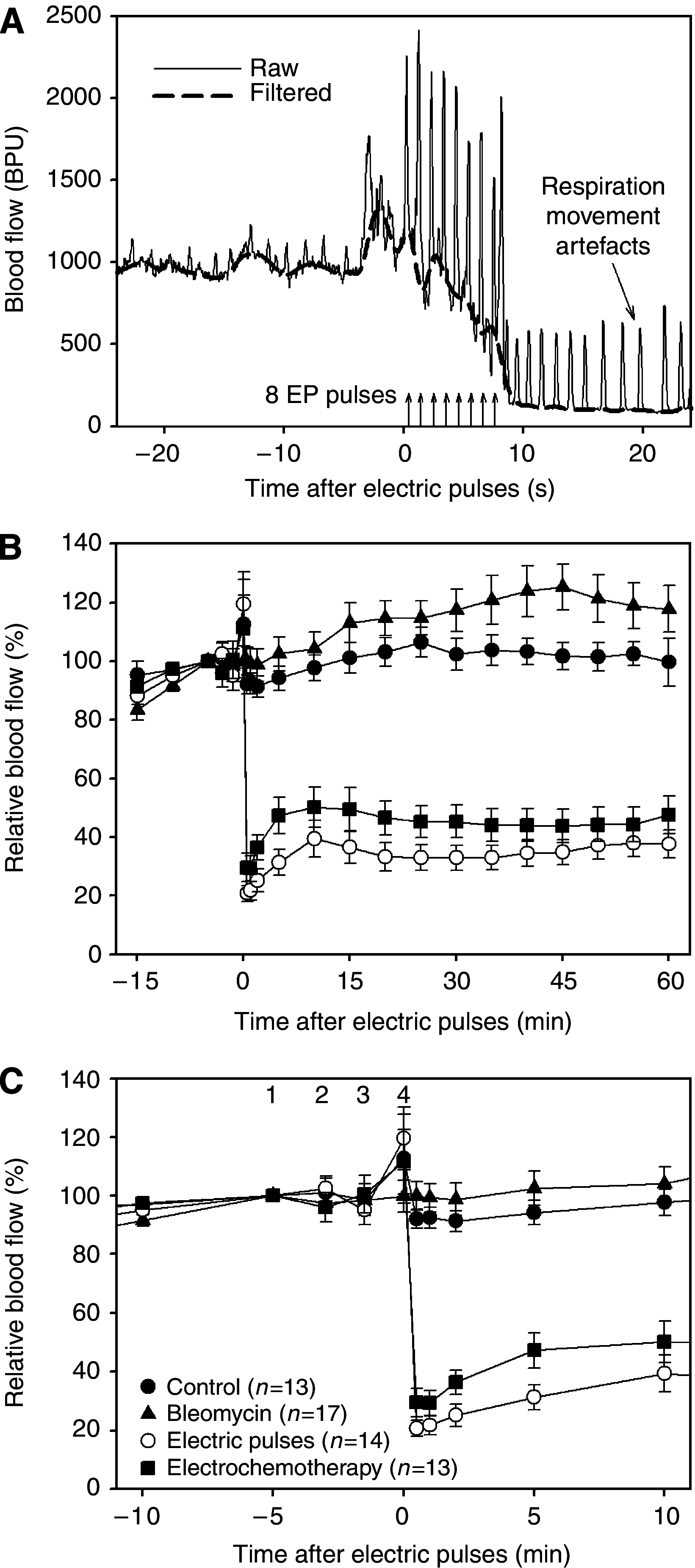
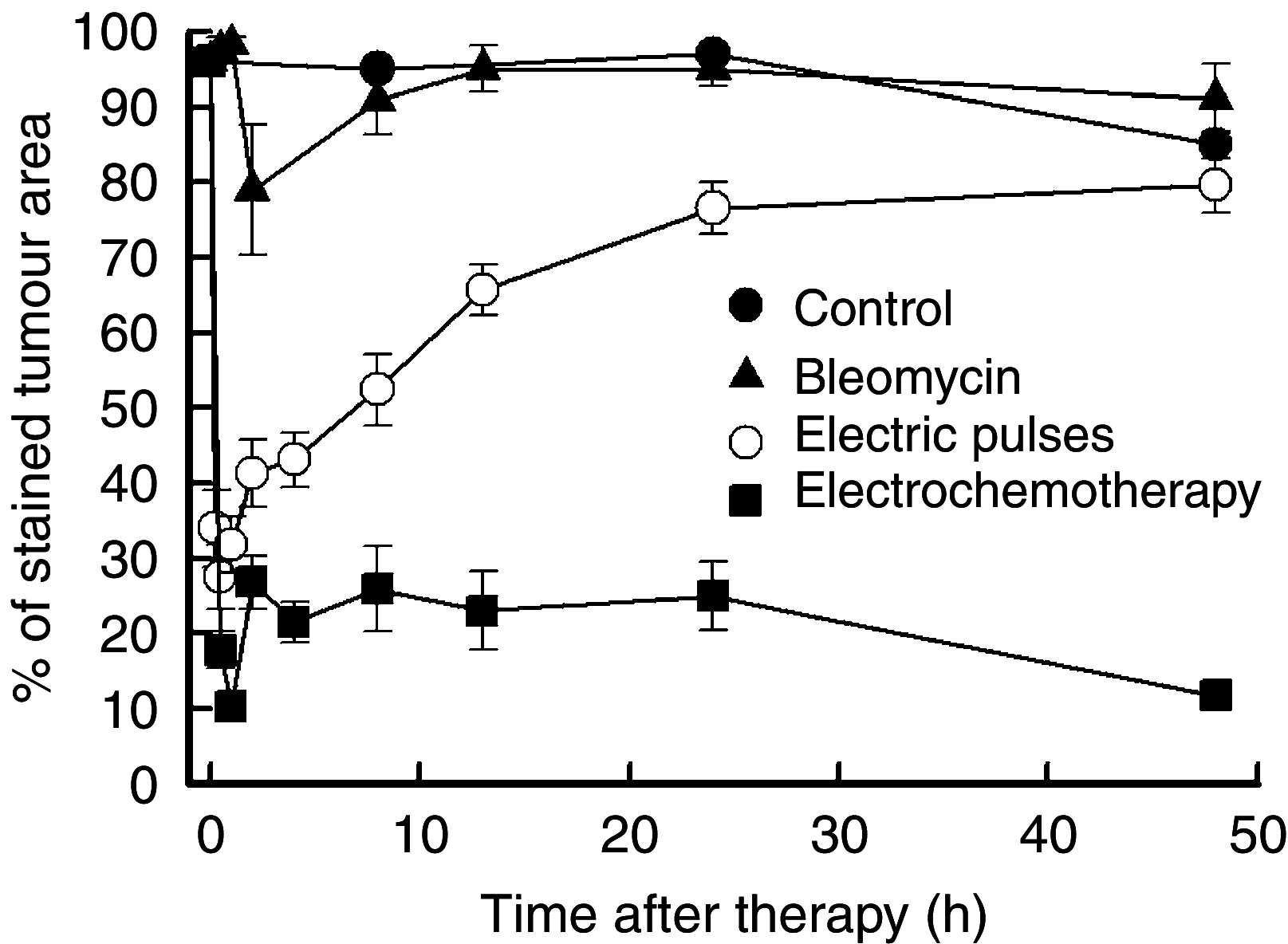
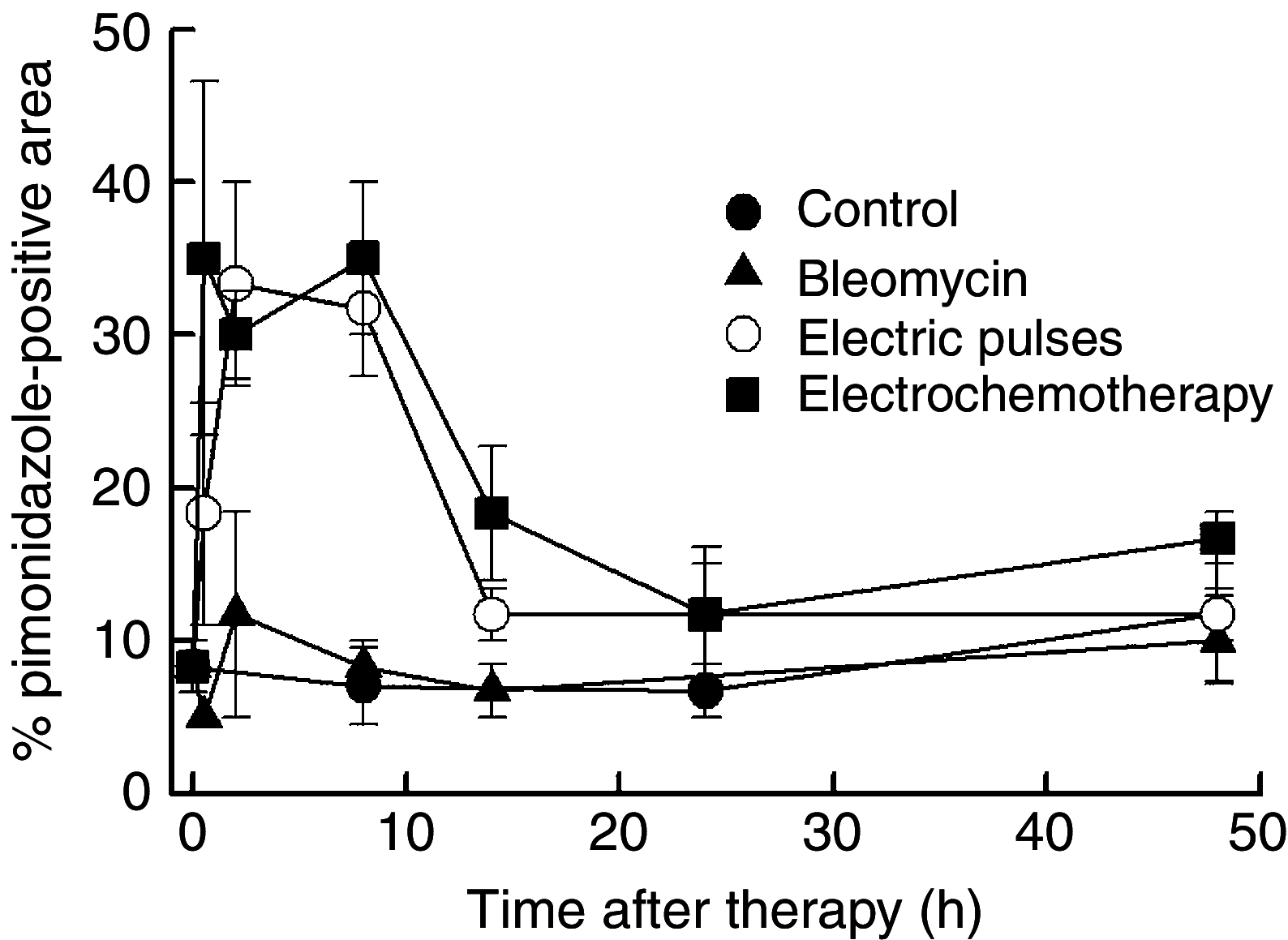
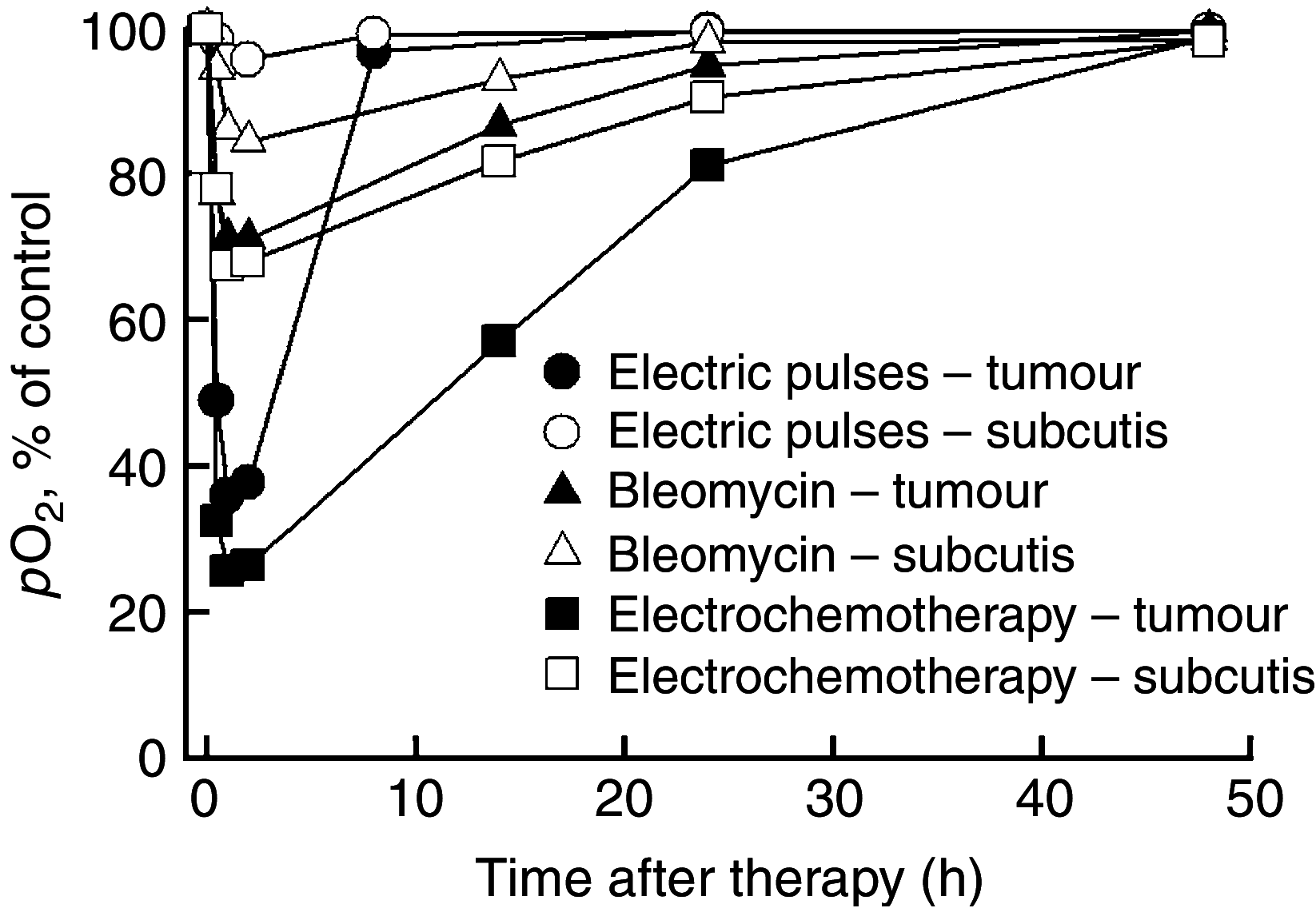
Electrochemotherapy has a direct cytotoxic effect on tumour cells, and presumably, a vascular disrupting effect. In this study, on the basis of the prediction of the mathematical model, histological evaluation and physiological measurements of the tumours were carried out to confirm that electroporation and electrochemotherapy of tumours have a vascular disrupting action. In the study, SA-1 solid subcutaneous sarcoma tumours in A/J mice were treated by bleomycin (BLM) given intravenously (1 mg kg(-1)), application of electric pulses (8 pulses, 1040 V, 100 micros, 1 Hz) or a combination of both - electrochemotherapy. The vascular effect was determined by laser Doppler flowmetry, power Doppler ultrasonographic imaging and Patent blue staining. The extent of tumour hypoxia was determined immunohistochemically by hypoxia marker pimonidazole and partial pressure of oxygen (pO(2)) in tumours by electron paramagnetic resonance oximetry. Electrochemotherapy with BLM induced good antitumour effect with 22 days, tumour growth delay and 38% tumour cures. The application of electric pulses to the tumours induced instant but transient tumour blood flow reduction (for 70%) that was recovered in 24 h. During this tumour blood flow reduction, we determined an increase in hypoxic tumour area for up to 30%, which was also reflected in reduced tumour oxygenation (for 70%). According to the described mathematical model, endothelial cells lining in tumour blood vessels are exposed to a approximately 40% higher electric field than the surrounding tumour cells, and therefore easily electroporated, allowing access of high BLM concentration to the cytosol. Consequently, electrochemotherapy has, besides the immediate vascular disrupting action, also a delayed one (after 24 h), as a consequence of endothelial cell swelling and apoptosis demonstrated by extensive tumour necrosis, tumour hypoxia, prolonged reduction of tumour blood flow and significant tumour growth delay, and tumour cures. Our results demonstrate that in addition to the well-established direct cytotoxic effect on tumour cells, electrochemotherapy also has an indirect vascular disrupting action resulting altogether in extensive tumour cell necrosis leading to complete regression of tumours.
Figures


References
-
- Belehradek Jr J, Orlowski S, Ramirez LH, Pron G, Poddevin B, Mir LM (1994) Electropermeabilization of cells and tissues assessed by the quantitative and qualitative electroloading of bleomycin. Biocim Biophys Acta 1190: 155–163 - PubMed
-
- Bokoch GM, Bohl BP, Chuang TH (1994) Guanine nucleotide exchange regulates membrane translocation of Rac/Fho GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 269: 31674–31679 - PubMed
-
- Cemazar M, Golzio M, Sersa G, Rols MP, Teissie J (2006) Electrically-assisted nucleic acids delivery to tissues in vivo: where do we stand? Curr Pharm Des 12: 3817–3825 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

