The relationship between alcohol consumption and glycemic control among patients with diabetes: the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Diabetes Registry
- PMID: 18183468
- PMCID: PMC2359478
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-007-0502-z
The relationship between alcohol consumption and glycemic control among patients with diabetes: the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Diabetes Registry
Abstract
Background: Alcohol consumption is a common behavior. Little is known about the relationship between alcohol consumption and glycemic control among people with diabetes.
Objective: To evaluate the association between alcohol consumption and glycemic control.
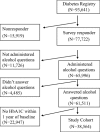
Design: Survey follow-up study, 1994-1997, among Kaiser Permanente Northern California members.
Patients: 38,564 adult diabetes patients.
Measurements: Self-reported alcohol consumption, and hemoglobin A1C (A1C), assessed within 1 year of survey date. Linear regression of A1C by alcohol consumption was performed, adjusted for sociodemographic variables, clinical variables, and diabetes disease severity. Least squares means estimates were derived.
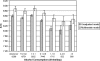
Results: In multivariate-adjusted models, A1C values were 8.88 (lifetime abstainers), 8.79 (former drinkers), 8.90 (<0.1 drink/day), 8.71 (0.1-0.9 drink/day), 8.51 (1-1.9 drinks/day), 8.39 (2-2.9 drinks/day), and 8.47 (>/=3 drinks/day). Alcohol consumption was linearly (p < 0.001) and inversely (p = 0.001) associated with A1C among diabetes patients.
Conclusions: Alcohol consumption is inversely associated with glycemic control among diabetes patients. This supports current clinical guidelines for moderate levels of alcohol consumption among diabetes patients. As glycemic control affects incidence of complications of diabetes, the lower A1C levels associated with moderate alcohol consumption may translate into lower risk for complications.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1001/jama.289.1.76', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.1.76'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12503980', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12503980/'}]}
- Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA. 2003;289:76–9. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9031031', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9031031/'}]}
- Armstrong DG, Lavery LA, van Houtum WH, Harkless LB. The impact of gender on amputation. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1997;36:66–9. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.2337/diacare.21.5.738', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.21.5.738'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9589233', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9589233/'}]}
- Morris AD, McAlpine R, Steinke D et al. Diabetes and lower-limb amputations in the community. A retrospective cohort study. DARTS/MEMO Collaboration. Diabetes Audit and Research in Tayside Scotland/Medicines Monitoring Unit. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:738–43. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.2337/diacare.6.1.87', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.6.1.87'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '6839926', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6839926/'}]}
- Most RS, Sinnock P. The epidemiology of lower extremity amputations in diabetic individuals. Diabetes Care. 1983;6:87–91. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.2337/diacare.16.1.16', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.16.1.16'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8422771', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8422771/'}]}
- Siitonen OI, Niskanen LK, Laakso M, Siitonen JT, Pyorala K. Lower-extremity amputations in diabetic and nondiabetic patients. A population-based study in eastern Finland. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:16–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

