A mechanism regulating the onset of Sox2 expression in the embryonic neural plate
- PMID: 18184035
- PMCID: PMC2174969
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060002
A mechanism regulating the onset of Sox2 expression in the embryonic neural plate
Abstract
In vertebrate embryos, the earliest definitive marker for the neural plate, which will give rise to the entire central nervous system, is the transcription factor Sox2. Although some of the extracellular signals that regulate neural plate fate have been identified, we know very little about the mechanisms controlling Sox2 expression and thus neural plate identity. Here, we use electroporation for gain- and loss-of-function in the chick embryo, in combination with bimolecular fluorescence complementation, two-hybrid screens, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and reporter assays to study protein interactions that regulate expression of N2, the earliest enhancer of Sox2 to be activated and which directs expression to the largest part of the neural plate. We show that interactions between three coiled-coil domain proteins (ERNI, Geminin, and BERT), the heterochromatin proteins HP1alpha and HP1gamma acting as repressors, and the chromatin-remodeling enzyme Brm acting as activator control the N2 enhancer. We propose that this mechanism regulates the timing of Sox2 expression as part of the process of establishing neural plate identity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
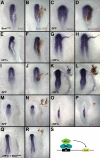
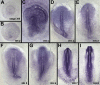



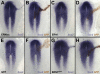

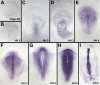




Similar articles
-
Epigenetic activation of Sox2 gene in the developing vertebrate neural plate.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jun 15;27(12):1921-7. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-01-0042. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27099369 Free PMC article.
-
Convergence of Wnt and FGF signals in the genesis of posterior neural plate through activation of the Sox2 enhancer N-1.Development. 2006 Jan;133(2):297-306. doi: 10.1242/dev.02196. Epub 2005 Dec 14. Development. 2006. PMID: 16354715
-
The Pou5f1/Pou3f-dependent but SoxB-independent regulation of conserved enhancer N2 initiates Sox2 expression during epiblast to neural plate stages in vertebrates.Dev Biol. 2011 Apr 15;352(2):354-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.12.027. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21185279
-
Mechanism of cell fate choice between neural and mesodermal development during early embryogenesis.Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2013 Jun;53(2):61-6. doi: 10.1111/cga.12017. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2013. PMID: 23751038 Review.
-
Developmental malformations of the eye: the role of PAX6, SOX2 and OTX2.Clin Genet. 2006 Jun;69(6):459-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00619.x. Clin Genet. 2006. PMID: 16712695 Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction of HP1 and Brg1/Brm with the globular domain of histone H3 is required for HP1-mediated repression.PLoS Genet. 2009 Dec;5(12):e1000769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000769. Epub 2009 Dec 11. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 20011120 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic figure ranking and user interfacing for intelligent figure search.PLoS One. 2010 Oct 7;5(10):e12983. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012983. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20949102 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of a biotinylatable Sox2 mouse model to identify Sox2 complexes in vivo.Transgenic Res. 2018 Feb;27(1):75-85. doi: 10.1007/s11248-018-0058-1. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Transgenic Res. 2018. PMID: 29383478 Free PMC article.
-
Geminin is required for the maintenance of pluripotency.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 19;8(9):e73826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073826. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24069236 Free PMC article.
-
Dual roles of Akirin2 protein during Xenopus neural development.J Biol Chem. 2017 Apr 7;292(14):5676-5684. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.777110. Epub 2017 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28193841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bylund M, Andersson E, Novitch BG, Muhr J. Vertebrate neurogenesis is counteracted by Sox1–3 activity. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:1162–1168. - PubMed
-
- Graham V, Khudyakov J, Ellis P, Pevny L. SOX2 functions to maintain neural progenitor identity. Neuron. 2003;39:749–765. - PubMed
-
- Ellis P, Fagan BM, Magness ST, Hutton S, Taranova O, et al. SOX2, a persistent marker for multipotential neural stem cells derived from embryonic stem cells, the embryo or the adult. Dev Neurosci. 2004;26:148–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

