Proteases for processing proneuropeptides into peptide neurotransmitters and hormones
- PMID: 18184105
- PMCID: PMC2731677
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094812
Proteases for processing proneuropeptides into peptide neurotransmitters and hormones
Abstract
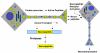
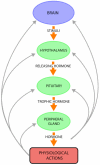
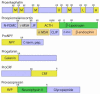
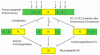
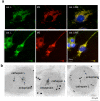
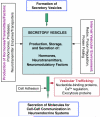
Peptide neurotransmitters and peptide hormones, collectively known as neuropeptides, are required for cell-cell communication in neurotransmission and for regulation of endocrine functions. Neuropeptides are synthesized from protein precursors (termed proneuropeptides or prohormones) that require proteolytic processing primarily within secretory vesicles that store and secrete the mature neuropeptides to control target cellular and organ systems. This review describes interdisciplinary strategies that have elucidated two primary protease pathways for prohormone processing consisting of the cysteine protease pathway mediated by secretory vesicle cathepsin L and the well-known subtilisin-like proprotein convertase pathway that together support neuropeptide biosynthesis. Importantly, this review discusses important areas of current and future biomedical neuropeptide research with respect to biological regulation, inhibitors, structural features of proneuropeptide and protease interactions, and peptidomics combined with proteomics for systems biological approaches. Future studies that gain in-depth understanding of protease mechanisms for generating active neuropeptides will be instrumental for translational research to develop pharmacological strategies for regulation of neuropeptide functions. Pharmacological applications for neuropeptide research may provide valuable therapeutics in health and disease.
Figures

References
Literature Cited
-
- Akil H, Watson SJ, Young E, Lewis ME, Khachaturian H, Walker JM. Endogenous opioids: biology and function. Ann. Re.v Neurosci. 1984;7:223–255. - PubMed
-
- Law PY, Loh HH. Regulation of opioid receptor activities. J Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999;289:607–624. - PubMed
-
- Roy S, Loh HH. Effects of opioids on the immune system. Neurochem. Res. 1996;21:1375–1386. - PubMed
-
- Felig Philip BJ, Frohman L. Endocrinology and Metabolism. McGraw-Hill Inc.; New York: 1981. pp. 293–297.
-
- Norris D. Vertebrate Endocrinology. Academic Press; San Diego: 1997. pp. 137–141.
Recommended Review Articles: Proteolytic Processing of Proneuropeptides
-
- Docherty K, Steiner DF. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. - PubMed
-
- Eipper BA, Stoffers DA, Mains RE. The biosynthesis of neuropeptides: peptide alpha-amidation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1992;15:57–85. - PubMed
-
- Fricker LD. Carboxypeptidase E. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1988;50:309–321. - PubMed
-
- Hook VY, Azaryan AV, Hwang SR, Tezapsidis N. Proteases and the emerging role of protease inhibitors in prohormone processing. FASEB J. 1994;8:1269–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

