Usefulness of manufactured tomato extracts in the diagnosis of tomato sensitization: Comparison with the prick-prick method
- PMID: 18184431
- PMCID: PMC2263074
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7961-6-1
Usefulness of manufactured tomato extracts in the diagnosis of tomato sensitization: Comparison with the prick-prick method
Abstract
Background: Commercial available skin prick test with fruits can be negative in sensitized or allergic patients due to a reduction in biological activity during the manufacturing process. Prick-prick tests with fresh foods are often preferred, but they are a non-standardized procedure. The usefulness of freeze-dried extracts of Canary Islands tomatoes, comparing the wheal sizes induced by prick test with the prick-prick method in the diagnosis of tomato sensitization has been analyzed.The objective of the study was to assess the potential diagnostic of freeze-dried extracts of Canary Islands tomatoes, comparing the wheal sizes induced by prick test with the prick-prick method.
Methods: Two groups of patients were analyzed: Group I: 26 individuals reporting clinical symptoms induced by tomato contact or ingestion. Group II: 71 control individuals with no symptoms induced by tomato: 12 of them were previously skin prick test positive to a tomato extract, 39 were atopic and 20 were non-atopic. All individuals underwent prick-prick with fresh ripe peel Canary tomatoes and skin prick tested with freeze-dried peel and pulp extracts obtained from peel and pulp of Canary tomatoes at 10 mg/ml. Wheal sizes and prick test positivity (>/= 7 mm2) were compared between groups.
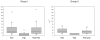
Results: In group I, 21 (81%) out of 26 patients were prick-prick positive. Twenty patients (77%) had positive skin prick test to peel extracts and 12 (46%) to pulp extracts. Prick-prick induced a mean wheal size of 43.81 +/- 40.19 mm2 compared with 44.25 +/- 36.68 mm2 induced by the peel extract (Not significant), and 17.79 +/- 9.39 mm2 induced by the pulp extract (p < 0.01).In group II, 13 (18%) out of 71 control patients were prick-prick positive. Twelve patients (all of them previously positive to peel extract) had positive skin prick test to peel and 3 to pulp. Prick-prick induced a mean wheal size of 28.88 +/- 13.12 mm2 compared with 33.17 +/- 17.55 mm2 induced by peel extract (Not significant), and 13.33 +/- 4.80 mm2 induced by pulp extract (p < 0.05 with peel extract and prick-prick).
Conclusion: Canary peel tomato extract seems to be as efficient as prick-prick tests with ripe tomatoes to diagnose patients sensitized to tomato. The wheal sizes induced by prick-prick and peel extracts were very similar and showed a high correlation coefficient.
Figures

References
-
- Bousquet J, Anto JM, Bachert C, Bousquet PJ, Colombo P, Crameri R, Daeron M, Fokkens W, Leynaert B, Lahoz C, Maurer M, Passalacqua G, Valenta R, van Hage M, Van Ree R. Factors responsible for differences between asymptomatic subjects and patients presenting an IgE sensitization to allergens. A GA2LEN project. Allergy. 2006;61:671–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01048.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asero R, Ballmer-Weber BK, Beyer K, Conti A, Dubakiene R, Fernandez-Rivas M, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Lidholm J, Mustakov T, Oude Elberink JN, Pumphrey RS, Stahl Skov P, van Ree R, Vlieg-Boerstra BJ, Hiller R, Hourihane JO, Kowalski M, Papadopoulos NG, Wal JM, Mills EN, Vieths S. IgE-Mediated food allergy diagnosis: Current status and new perspectives. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007;51:135–47. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200600132. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferrer A, Carnés J, Gallego MT, Andreu C, Fernández-Caldas E. Characterization and improvement of apple extracts for the diagnosisof apple IgE-mediated allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;95:462–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

