From neuronal activity to the actin cytoskeleton: a role for CaMKKs and betaPIX in spine morphogenesis
- PMID: 18184558
- PMCID: PMC5405797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.12.017
From neuronal activity to the actin cytoskeleton: a role for CaMKKs and betaPIX in spine morphogenesis
Abstract
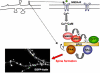
Electrical activity plays a crucial role in neuronal circuit assembly. Activation of NMDA receptors induces the elevation of intracellular calcium, resulting in the modulation of calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs). The CaMK pathway regulates synaptogenesis by driving the formation of dendritic spines. However, the molecular effectors downstream of this pathway have remained poorly defined. In this issue of Neuron, Saneyoshi et al. identify a new signaling complex containing CaMKK/CaMKI/betaPIX/Rac that regulates the morphogenesis of spines in an activity-dependent manner.
Figures
Comment on
-
Activity-dependent synaptogenesis: regulation by a CaM-kinase kinase/CaM-kinase I/betaPIX signaling complex.Neuron. 2008 Jan 10;57(1):94-107. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.016. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18184567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carlisle HJ, Kennedy MB. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:182–187. - PubMed
-
- Nimchinsky EA, Sabatini BL, Svoboda K. Structure and function of dendritic spines. Annu Rev Physiol. 2002;64:313–353. - PubMed
-
- Segura I, Essmann CL, Weinges S, Acker-Palmer A. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:301–310. - PubMed
-
- Soderling TR. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000;10:375–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

