Members of the miRNA-200 family regulate olfactory neurogenesis
- PMID: 18184563
- PMCID: PMC2204047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.018
Members of the miRNA-200 family regulate olfactory neurogenesis
Abstract
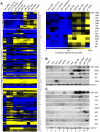
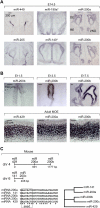
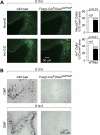
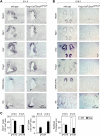
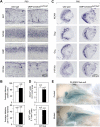
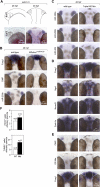
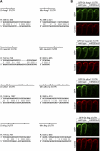
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are highly expressed in vertebrate neural tissues, but the contribution of specific miRNAs to the development and function of different neuronal populations is still largely unknown. We report that miRNAs are required for terminal differentiation of olfactory precursors in both mouse and zebrafish but are dispensable for proper function of mature olfactory neurons. The repertoire of miRNAs expressed in olfactory tissues contains over 100 distinct miRNAs. A subset, including the miR-200 family, shows high olfactory enrichment and expression patterns consistent with a role during olfactory neurogenesis. Loss of function of the miR-200 family phenocopies the terminal differentiation defect observed in absence of all miRNA activity in olfactory progenitors. Our data support the notion that vertebrate tissue differentiation is controlled by conserved subsets of organ-specific miRNAs in both mouse and zebrafish and provide insights into control mechanisms underlying olfactory differentiation in vertebrates.
Figures

References
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Beites C.L., Kawauchi S., Crocker C.E., Calof A.L. Identification and molecular regulation of neural stem cells in the olfactory epithelium. Exp. Cell Res. 2005;306:309–316. - PubMed
-
- Belluscio L., Koentges G., Axel R., Dulac C. A map of pheromone receptor activation in the mammalian brain. Cell. 1999;97:209–220. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E., Caudy A.A., Hammond S.M., Hannon G.J. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

