Activity-dependent synaptogenesis: regulation by a CaM-kinase kinase/CaM-kinase I/betaPIX signaling complex
- PMID: 18184567
- PMCID: PMC2277504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.016
Activity-dependent synaptogenesis: regulation by a CaM-kinase kinase/CaM-kinase I/betaPIX signaling complex
Abstract
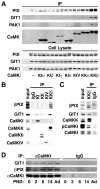
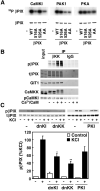
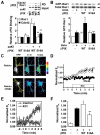
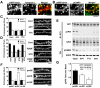
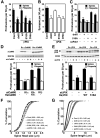
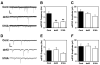
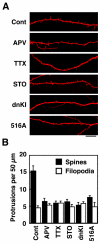
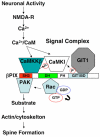
Neuronal activity augments maturation of mushroom-shaped spines to form excitatory synapses, thereby strengthening synaptic transmission. We have delineated a Ca(2+)-signaling pathway downstream of the NMDA receptor that stimulates calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase (CaMKK) and CaMKI to promote formation of spines and synapses in hippocampal neurons. CaMKK and CaMKI form a multiprotein signaling complex with the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) betaPIX and GIT1 that is localized in spines. CaMKI-mediated phosphorylation of Ser516 in betaPIX enhances its GEF activity, resulting in activation of Rac1, an established enhancer of spinogenesis. Suppression of CaMKK or CaMKI by pharmacological inhibitors, dominant-negative (dn) constructs and siRNAs, as well as expression of the betaPIX Ser516Ala mutant, decreases spine formation and mEPSC frequency. Constitutively-active Pak1, a downstream effector of Rac1, rescues spine inhibition by dnCaMKI or betaPIX S516A. This activity-dependent signaling pathway can promote synapse formation during neuronal development and in structural plasticity.
Figures
Comment in
-
From neuronal activity to the actin cytoskeleton: a role for CaMKKs and betaPIX in spine morphogenesis.Neuron. 2008 Jan 10;57(1):3-4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.12.017. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18184558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackermann M, Matus A. Activity-induced targeting of profilin and stabilization of dendritic spine morphology. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:1194–1200. - PubMed
-
- Audebert S, Navarro C, Nourry C, Chasserot-Golaz S, Lecine P, Bellaiche Y, Dupont JL, Premont RT, Sempere C, Strub JM, et al. Mammalian Scribble forms a tight complex with the betaPIX exchange factor. Curr Biol. 2004;14:987–995. - PubMed
-
- Bahr BA. Long-term hippocampal slices: a model system for investigating synaptic mechanisms and pathologic processes. J Neurosci Res. 1995;42:294–305. - PubMed
-
- Bokoch GM. Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:743–781. - PubMed
-
- Bonhoeffer T, Yuste R. Spine motility. Phenomenology, mechanisms, and function. Neuron. 2002;35:1019–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

