The plant defense elicitor cryptogein stimulates clathrin-mediated endocytosis correlated with reactive oxygen species production in bright yellow-2 tobacco cells
- PMID: 18184734
- PMCID: PMC2259092
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.111716
The plant defense elicitor cryptogein stimulates clathrin-mediated endocytosis correlated with reactive oxygen species production in bright yellow-2 tobacco cells
Abstract
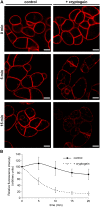
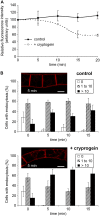
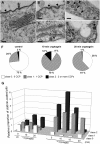
The plant defense elicitor cryptogein triggers well-known biochemical events of early signal transduction at the plasma membrane of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) cells, but microscopic observations of cell responses related to these early events were lacking. We determined that internalization of the lipophilic dye FM4-64, which is a marker of endocytosis, is stimulated a few minutes after addition of cryptogein to tobacco Bright Yellow-2 (BY-2) cells. This stimulation is specific to the signal transduction pathway elicited by cryptogein because a lipid transfer protein, which binds to the same receptor as cryptogein but without triggering signaling, does not increase endocytosis. To define the nature of the stimulated endocytosis, we quantified clathrin-coated pits (CCPs) forming on the plasma membrane of BY-2 cells. A transitory stimulation of this morphological event by cryptogein occurs within the first 15 min. In the presence of cryptogein, increases in both FM4-64 internalization and clathrin-mediated endocytosis are specifically blocked upon treatment with 5 microm tyrphostin A23, a receptor-mediated endocytosis inhibitor. The kinetics of the transient increase in CCPs at the plasma membrane coincides with that of transitory reactive oxygen species (ROS) production occurring within the first 15 min after elicitation. Moreover, in BY-2 cells expressing NtrbohD antisense cDNA, which are unable to produce ROS when treated with cryptogein, the CCP stimulation is inhibited. These results indicate that the very early endocytic process induced by cryptogein in tobacco is due, at least partly, to clathrin-mediated endocytosis and is dependent on ROS production by the NADPH oxidase NtrbohD.
Figures
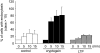
Similar articles
-
Long-chain bases and their phosphorylated derivatives differentially regulate cryptogein-induced production of reactive oxygen species in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) BY-2 cells.New Phytol. 2015 Feb;205(3):1239-1249. doi: 10.1111/nph.13094. Epub 2014 Oct 10. New Phytol. 2015. PMID: 25303640
-
NADPH oxidase-mediated reactive oxygen species production: subcellular localization and reassessment of its role in plant defense.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2009 Jul;22(7):868-81. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-22-7-0868. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2009. PMID: 19522569
-
Phosphoproteins involved in the signal transduction of cryptogein, an elicitor of defense reactions in tobacco.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2000 Aug;13(8):821-9. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.8.821. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2000. PMID: 10939253
-
Involvement of plasma membrane proteins in plant defense responses. Analysis of the cryptogein signal transduction in tobacco.Biochimie. 1999 Jun;81(6):663-8. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(99)80123-0. Biochimie. 1999. PMID: 10433120 Review.
-
Clathrin-mediated endocytosis: membrane factors pull the trigger.Trends Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;11(9):385-91. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(01)02082-7. Trends Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11514193 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of the cryptogein gene to stimulate the accumulation of Bacopa saponins in transgenic Bacopa monnieri plants.Plant Cell Rep. 2012 Oct;31(10):1899-909. doi: 10.1007/s00299-012-1303-3. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Plant Cell Rep. 2012. Retraction in: Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 24;43(9):221. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03309-5. PMID: 22733208 Retracted.
-
Apoplastic Cell Death-Inducing Proteins of Filamentous Plant Pathogens: Roles in Plant-Pathogen Interactions.Front Genet. 2020 Jun 26;11:661. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00661. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32676100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative proteomics reveals a dynamic association of proteins to detergent-resistant membranes upon elicitor signaling in tobacco.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 Sep;8(9):2186-98. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900090-MCP200. Epub 2009 Jun 13. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19525550 Free PMC article.
-
Drought stress stimulates endocytosis and modifies membrane lipid order of rhizodermal cells of Medicago truncatula in a genotype-dependent manner.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 May 28;19(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1814-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31138155 Free PMC article.
-
Plant receptors go endosomal: a moving view on signal transduction.Plant Physiol. 2008 Aug;147(4):1565-74. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.120287. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18678748 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Banbury DN, Oakley JD, Sessions RB, Banting G (2003) Tyrphostin A23 inhibits internalization of the transferrin receptor by perturbing the interaction between tyrosine motifs and the medium chain subunit of the AP-2 adaptor complex. J Biol Chem 278 12022–12028 - PubMed
-
- Betz WJ, Mao F, Smith CB (1996) Imaging exocytosis and endocytosis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 6 365–371 - PubMed
-
- Blein JP, Coutos-Thévenot P, Marion D, Ponchet M (2002) From elicitins to lipid-transfer proteins: a new insight in cell signalling involved in plant defence mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci 7 293–296 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

