Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway accelerates bone regeneration
- PMID: 18184809
- PMCID: PMC2206597
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0708474105
Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway accelerates bone regeneration
Abstract
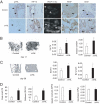
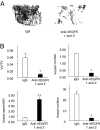
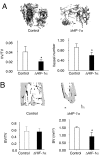
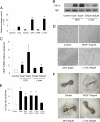
The hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) pathway is the central regulator of adaptive responses to low oxygen availability and is required for normal skeletal development. Here, we demonstrate that the HIF-1alpha pathway is activated during bone repair and can be manipulated genetically and pharmacologically to improve skeletal healing. Mice lacking pVHL in osteoblasts with constitutive HIF-1alpha activation in osteoblasts had markedly increased vascularity and produced more bone in response to distraction osteogenesis, whereas mice lacking HIF-1alpha in osteoblasts had impaired angiogenesis and bone healing. The increased vascularity and bone regeneration in the pVHL mutants were VEGF dependent and eliminated by concomitant administration of VEGF receptor antibodies. Small-molecule inhibitors of HIF prolyl hydroxylation stabilized HIF/VEGF production and increased angiogenesis in vitro. One of these molecules (DFO) administered in vivo into the distraction gap increased angiogenesis and markedly improved bone regeneration. These results identify the HIF-1alpha pathway as a critical mediator of neoangiogenesis required for skeletal regeneration and suggest the application of HIF activators as therapies to improve bone healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATF4 promotes bone angiogenesis by increasing VEGF expression and release in the bone environment.J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Sep;28(9):1870-1884. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1958. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 23649506 Free PMC article.
-
[Regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha on osteoblast function in osteogenesis].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Dec 18;87(47):3357-61. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18478952 Chinese.
-
Salidroside improves angiogenesis-osteogenesis coupling by regulating the HIF-1α/VEGF signalling pathway in the bone environment.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;884:173394. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173394. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32730833
-
Oxygen sensing and osteogenesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1117:1-11. doi: 10.1196/annals.1402.049. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18056033 Review.
-
Fetal growth plate: a developmental model of cellular adaptation to hypoxia.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1117:26-39. doi: 10.1196/annals.1402.076. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18056035 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase enhances the dentin-pulp complex regeneration mediated by crosstalk between vascular endothelial cells and dental pulp stem cells.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 16;22(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04863-y. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38229161 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoblast-Osteoclast Coculture Amplifies Inhibitory Effects of FG-4592 on Human Osteoclastogenesis and Reduces Bone Resorption.JBMR Plus. 2020 May 14;4(7):e10370. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10370. eCollection 2020 Jul. JBMR Plus. 2020. PMID: 32666021 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo and in vitro characteristic of HIF-1α and relative genes in ischemic femoral head necrosis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):7210-6. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261616 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental study of the effects of hypoxia simulator on osteointegration of titanium prosthesis in osteoporotic rats.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Nov 11;22(1):944. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04777-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34763682 Free PMC article.
-
Bone biology: Vessels of rejuvenation.Nature. 2014 Mar 20;507(7492):313-4. doi: 10.1038/nature13210. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24646993 No abstract available.
References
-
- Einhorn TA. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:940–956. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson C, Alpern E, Miclau T, Helms JA. Mech Dev. 1999;87:57–66. - PubMed
-
- Gerstenfeld LC, Cullinane DM, Barnes GL, Graves DT, Einhorn TA. J Cell Biochem. 2003;88:873–884. - PubMed
-
- Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ, Tepper OM, Bastidas N, Kleinman ME, Capla JM, Galiano RD, Levine JP, Gurtner GC. Nat Med. 2004;10:858–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

