High-frequency HTR3B variant associated with major depression dramatically augments the signaling of the human 5-HT3AB receptor
- PMID: 18184810
- PMCID: PMC2206603
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0708454105
High-frequency HTR3B variant associated with major depression dramatically augments the signaling of the human 5-HT3AB receptor
Abstract
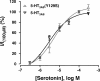
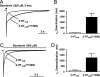
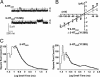
The 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 (5-HT3) receptor mediates the fast excitatory neurotransmission of serotonin and is known to mediate the nausea/emesis induced by radio/chemotherapy and anesthetics. A polymorphism encoding the variation Y129S in the 5-HT3B subunit exists in high frequency in the general population and has been shown to be inversely correlated to the incidence of major depression in women. We show that 5-HT3AB(Y129S) receptors exhibit a substantially increased maximal response to serotonin compared with WT receptors in two fluorescence-based cellular assays. In electrophysiological recordings, the deactivation and desensitization kinetics of the 5-HT3AB(Y129S) receptor are 20- and 10-fold slower, respectively, than those of the WT receptor. Single-channel measurements reveal a 7-fold-increased mean open time of 5-HT3AB(Y129S) receptors compared with WT receptors. The augmented signaling displayed by 5-HT3AB(Y129S) receptors may confer protection against the development of depression. The variant also may influence the development and/or treatment of nausea and other disorders involving 5-HT3 receptors. Thus, the impact of the high-frequency variant 5-HT3B(Y129S) on 5-HT3AB receptor signaling calls for a search for additional phenotypes, and the variant may thus aid in establishing the role of the 5-HT3AB receptor in pathophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
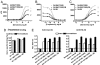
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the effects of four HTR3B polymorphisms on human 5-HT3AB receptor expression and signalling.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008 Dec;18(12):1027-40. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e328310f950. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008. PMID: 19008750
-
Naturally occurring variations in the human 5-HT3A gene profoundly impact 5-HT3 receptor function and expression.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2007 Apr;17(4):255-66. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3280117269. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17496724
-
Naturally occurring variants in the HTR3B gene significantly alter properties of human heteromeric 5-hydroxytryptamine-3A/B receptors.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008 Sep;18(9):793-802. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283050117. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18698232
-
The auspicious role of the 5-HT3 receptor in depression: a probable neuronal target?J Psychopharmacol. 2010 Apr;24(4):455-69. doi: 10.1177/0269881109348161. Epub 2010 Feb 1. J Psychopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20123937 Review.
-
Serotonin type 3 receptor genes: HTR3A, B, C, D, E.Pharmacogenomics. 2008 May;9(5):501-4. doi: 10.2217/14622416.9.5.501. Pharmacogenomics. 2008. PMID: 18466097 Review.
Cited by
-
Allosteric modulation of an excitatory amino acid transporter: the subtype-selective inhibitor UCPH-101 exerts sustained inhibition of EAAT1 through an intramonomeric site in the trimerization domain.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 16;33(3):1068-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3396-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23325245 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized trial evaluating the association between related gene polymorphism and nausea and vomiting induced by cisplatin multi-day chemotherapy.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Nov 3;16(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01719-0. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37924126 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Susceptibility loci for heroin and cocaine addiction in the serotonergic and adrenergic pathways in populations of different ancestry.Pharmacogenomics. 2015;16(12):1329-42. doi: 10.2217/pgs.15.86. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Pharmacogenomics. 2015. PMID: 26227246 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxy Pentacyclic Triterpene Acid, Kaempferol, Inhibits the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine Type 3A Receptor Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 4;23(1):544. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010544. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35008969 Free PMC article.
-
Association and interaction analyses of 5-HT3 receptor and serotonin transporter genes with alcohol, cocaine, and nicotine dependence using the SAGE data.Hum Genet. 2014 Jul;133(7):905-18. doi: 10.1007/s00439-014-1431-7. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24590108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lucki I. Biol Psychiatry. 1998;44:151–162. - PubMed
-
- Hoyer D, Hannon JP, Martin GR. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2002;71:533–554. - PubMed
-
- Turner TJ, Mokler DJ, Luebke JI. Neuroscience. 2004;129:703–718. - PubMed
-
- Funahashi M, Mitoh Y, Matsuo R. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2004;26:615–622. - PubMed
-
- Dremencov E, Weizmann Y, Kinor N, Gispan-Herman I, Yadid G. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7:165–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

