Cooperative binding of ATP and RNA induces a closed conformation in a DEAD box RNA helicase
- PMID: 18184816
- PMCID: PMC2206573
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705488105
Cooperative binding of ATP and RNA induces a closed conformation in a DEAD box RNA helicase
Abstract
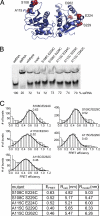
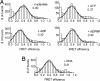
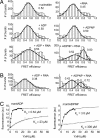
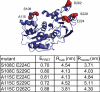
RNA helicases couple the energy from ATP hydrolysis with structural changes of their RNA substrates. DEAD box helicases form the largest class of RNA helicases and share a helicase core comprising two RecA-like domains. An opening and closing of the interdomain cleft during RNA unwinding has been postulated but not shown experimentally. Single-molecule FRET experiments with the Bacillus subtilis DEAD box helicase YxiN carrying donor and acceptor fluorophores on different sides of the interdomain cleft reveal an open helicase conformation in the absence of nucleotides, or in the presence of ATP, or ADP, or RNA. In the presence of ADP and RNA, the open conformation is retained. By contrast, cooperative binding of ATP and RNA leads to a compact helicase structure, proving that the ATP- and ADP-bound states of RNA helicases display substantially different structures only when the RNA substrate is bound. These results establish a closure of the interdomain cleft in the helicase core at the beginning of the unwinding reaction, and suggest a conserved mechanism of energy conversion among DEAD box helicases across kingdoms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The DEAD box helicase YxiN maintains a closed conformation during ATP hydrolysis.Biochemistry. 2009 Nov 17;48(45):10679-81. doi: 10.1021/bi901278p. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19839642
-
Authentic interdomain communication in an RNA helicase reconstituted by expressed protein ligation of two helicase domains.FEBS J. 2007 Jan;274(2):463-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05593.x. FEBS J. 2007. PMID: 17229151
-
A structural model for the DEAD box helicase YxiN in solution: localization of the RNA binding domain.J Mol Biol. 2010 Oct 1;402(4):629-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.07.049. Epub 2010 Aug 5. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20691700
-
Fluorescence methods in the investigation of the DEAD-box helicase mechanism.Exp Suppl. 2014;105:161-92. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-0856-9_8. Exp Suppl. 2014. PMID: 25095995 Review.
-
The mechanism of ATP-dependent RNA unwinding by DEAD box proteins.Biol Chem. 2009 Dec;390(12):1237-50. doi: 10.1515/BC.2009.135. Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19747077 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of DEAD-box proteins in RNA and RNP Folding.RNA Biol. 2010 Nov-Dec;7(6):667-76. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.6.13571. Epub 2010 Nov 1. RNA Biol. 2010. PMID: 21045543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular dynamics simulation of the allosteric regulation of eIF4A protein from the open to closed state, induced by ATP and RNA substrates.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 23;9(1):e86104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086104. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465900 Free PMC article.
-
Gyrase containing a single C-terminal domain catalyzes negative supercoiling of DNA by decreasing the linking number in steps of two.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 27;46(13):6773-6784. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky470. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29893908 Free PMC article.
-
eIF4B stimulates eIF4A ATPase and unwinding activities by direct interaction through its 7-repeats region.RNA Biol. 2017 Jan 2;14(1):113-123. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1259782. Epub 2016 Nov 18. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27858515 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics and Thermodynamics of DbpA Protein's C-Terminal Domain Interaction with RNA.ACS Omega. 2017 Nov 30;2(11):8033-8038. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b01205. Epub 2017 Nov 16. ACS Omega. 2017. PMID: 29214235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cordin O, Banroques J, Tanner NK, Linder P. Gene. 2006;367:17–37. - PubMed
-
- Rogers GW, Jr, Richter NJ, Merrick WC. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:12236–12244. - PubMed
-
- Yang Q, Jankowsky E. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13:981–986. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph MG, Heissmann R, Wittmann JG, Klostermeier D. J Mol Biol. 2006;361:731–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

