Noise in solid-state nanopores
- PMID: 18184817
- PMCID: PMC2206550
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705349105
Noise in solid-state nanopores
Abstract
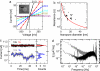
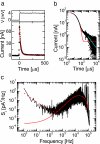
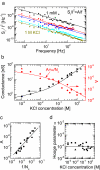
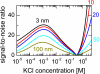
We study ionic current fluctuations in solid-state nanopores over a wide frequency range and present a complete description of the noise characteristics. At low frequencies (f approximately < 100 Hz) we observe 1/f-type of noise. We analyze this low-frequency noise at different salt concentrations and find that the noise power remarkably scales linearly with the inverse number of charge carriers, in agreement with Hooge's relation. We find a Hooge parameter alpha = (1.1 +/- 0.1) x 10(-4). In the high-frequency regime (f approximately > 1 kHz), we can model the increase in current power spectral density with frequency through a calculation of the Johnson noise. Finally, we use these results to compute the signal-to-noise ratio for DNA translocation for different salt concentrations and nanopore diameters, yielding the parameters for optimal detection efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

