Passive transfer of maternal Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae-specific cellular immunity to piglets
- PMID: 18184823
- PMCID: PMC2268269
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00466-07
Passive transfer of maternal Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae-specific cellular immunity to piglets
Abstract
Immunity in the neonatal animal is primarily maternally derived, either by lymphocytes that pass into the newborn across the placenta or following colostrum ingestion. However, the effect of this passively transferred cellular maternal immunity on the newborn's immune repertoire is not clearly understood. Various studies have shown that colostral lymphocytes are activated and possess functional abilities; however, no studies have shown the transfer of colostral antigen-specific T-cell-specific responses in a newborn. In this study we examined the transfer of vaccine-induced Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae cellular immunity from immune dams to newborn piglets. Newborn piglets from vaccinated and nonvaccinated dams were assessed in two ways for cellular immune responses specific to M. hyopneumoniae: (i) delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) testing and (ii) in vitro lymphocyte proliferation, assayed on piglet blood lymphocytes and sow colostral lymphocytes. DTH responses to M. hyopneumoniae were detected only for offspring of vaccinated sows, whereas DTH responses to the nonspecific mitogen phytohemagglutinin were seen for all piglets. M. hyopneumoniae-specific proliferation was seen for colostral lymphocytes from vaccinated sows and for blood lymphocytes from neonatal piglets of vaccinated dams but not for blood lymphocytes from piglets of nonvaccinated sows. Functional antigen-specific T cells were transferred to offspring from vaccinated sows and participated in the neonatal immune response upon stimulation. These data have implications for defining disease intervention strategies.
Figures
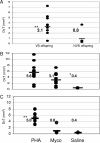
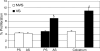
Similar articles
-
Transfer of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae-specific cell mediated immunity to neonatal piglets.Vet Res. 2021 Jun 30;52(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-00968-0. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34193259 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal immunity enhances Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccination induced cell-mediated immune responses in piglets.BMC Vet Res. 2014 Jun 5;10:124. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-10-124. BMC Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 24903770 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody response to Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection in vaccinated pigs with or without maternal antibodies induced by sow vaccination.J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2006 Jun;53(5):229-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.2006.00952.x. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2006. PMID: 16732881
-
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae: from disease to vaccine development.Vet Microbiol. 2013 Aug 30;165(3-4):234-42. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Vet Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23680109 Review.
-
Acclimation strategies in gilts to control Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection.Vet Microbiol. 2018 Jun;219:23-29. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Vet Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29778201 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of two intramuscular combined vaccines for the control of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and porcine circovirus type 2 in growing pigs: a randomized field trial.Porcine Health Manag. 2021 Jun 27;7(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s40813-021-00220-3. Porcine Health Manag. 2021. PMID: 34176520 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of PRRSv specific, maternally derived and induced immune response in Ingelvac PRRSFLEX EU vaccinated piglets in the presence of maternally transferred immunity.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 2;14(10):e0223060. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223060. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31577832 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular adaptive immune response against porcine circovirus type 2 in subclinically infected pigs.BMC Vet Res. 2009 Dec 22;5:45. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-5-45. BMC Vet Res. 2009. PMID: 20028550 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae-specific cell mediated immunity to neonatal piglets.Vet Res. 2021 Jun 30;52(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-00968-0. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34193259 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal immunity enhances Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccination induced cell-mediated immune responses in piglets.BMC Vet Res. 2014 Jun 5;10:124. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-10-124. BMC Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 24903770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adegboye, D. S. 1978. Attempts to demonstrate cell-mediated immune responses during Mycoplasma suipneumoniae infection of pigs. Res. Vet. Sci. 25:323-330. - PubMed
-
- Bautista, A. E., M. P. Suarez, and T. W. Molitor. 1999. Cell-mediated immunity to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in swine. Arch. Virol. 144:117-134. - PubMed
-
- Evans, P. A., T. J. Newby, C. R. Stokes, and F. J. Bourne. 1982. A study of cells in the mammary secretions of sows. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 3:515-527. - PubMed
-
- Grosse Beilage, E., and A. Schreiber. 2005. Vaccination of sows against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae with Hyoresp. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 112:256-261. (Abstract.) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

