Asialoerythropoietin prevents contrast-induced nephropathy
- PMID: 18184858
- PMCID: PMC2396737
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2007040481
Asialoerythropoietin prevents contrast-induced nephropathy
Abstract
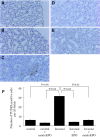
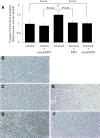
Strategies to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) are suboptimal. Erythropoietin was recently found to be cytoprotective in a variety of nonhematopoietic cells, so it was hypothesized that the nonhematopoietic erythropoietin derivative asialoerythropoietin would prevent CIN. Nephropathy was induced in rats by injection of the radiocontrast medium Ioversol in addition to inhibition of prostaglandin and nitric oxide synthesis. Administration of a single dose of asialoerythropoietin before the induction of nephropathy significantly attenuated the resulting renal dysfunction and histologic renal tubular injury. Contrast-induced apoptosis of renal tubular cells was inhibited by asialoerythropoietin both in vivo and in vitro, and this effect was blocked by a Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) inhibitor in vitro. Furthermore, phospho-JAK2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) and heat-shock protein 70 increased after injection of asialoerythropoietin, suggesting that the effects of asialoerythropoietin may be mediated by the activation of the JAK2/STAT5 pathway. Overall, these findings suggest that asialoerythropoietin may have potential as a new therapeutic approach to prevent CIN given its ability to preserve renal function and directly protect renal tissue.
Figures




References
-
- Finn WF: The clinical and renal consequences of contrast-induced nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21: i2–i10, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Tepel M, Aspelin P, Lameire N: Contrast-induced nephropathy: A clinical and evidence-based approach. Circulation 113: 1799–1806, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Mehran R, Nikolsky E: Contrast-induced nephropathy: Definition, epidemiology, and patients at risk. Kidney Int Suppl 11–15, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Briguori C, Marenzi G: Contrast-induced nephropathy: Pharmacological prophylaxis. Kidney Int Suppl 30–38, 2006 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

