Pathway analysis of primary central nervous system lymphoma
- PMID: 18184868
- PMCID: PMC2265457
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-119099
Pathway analysis of primary central nervous system lymphoma
Abstract
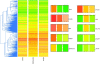
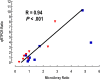
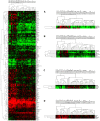
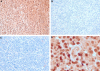
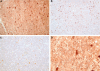
Primary central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma (PCNSL) is a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) confined to the CNS. A genome-wide gene expression comparison between PCNSL and non-CNS DLBCL was performed, the latter consisting of both nodal and extranodal DLBCL (nDLBCL and enDLBCL), to identify a "CNS signature." Pathway analysis with the program SigPathway revealed that PCNSL is characterized notably by significant differential expression of multiple extracellular matrix (ECM) and adhesion-related pathways. The most significantly up-regulated gene is the ECM-related osteopontin (SPP1). Expression at the protein level of ECM-related SPP1 and CHI3L1 in PCNSL cells was demonstrated by immunohistochemistry. The alterations in gene expression can be interpreted within several biologic contexts with implications for PCNSL, including CNS tropism (ECM and adhesion-related pathways, SPP1, DDR1), B-cell migration (CXCL13, SPP1), activated B-cell subtype (MUM1), lymphoproliferation (SPP1, TCL1A, CHI3L1), aggressive clinical behavior (SPP1, CHI3L1, MUM1), and aggressive metastatic cancer phenotype (SPP1, CHI3L1). The gene expression signature discovered in our study may represent a true "CNS signature" because we contrasted PCNSL with wide-spectrum non-CNS DLBCL on a genomic scale and performed an in-depth bioinformatic analysis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Differential gene expression in central nervous system lymphoma.Blood. 2009 Jan 1;113(1):266-7; author reply 267-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-152835. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19122120 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Anthony IC, Crawford DH, Bell JE. B lymphocytes in the normal brain: contrasts with HIV-associated lymphoid infiltrates and lymphomas. Brain. 2003;126:1058–1067. - PubMed
-
- Braaten KM, Betensky RA, de Leval L, et al. BCL-6 expression predicts improved survival in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:1063–1069. - PubMed
-
- Larocca LM, Capello D, Rinelli A, et al. The molecular and phenotypic profile of primary central nervous system lymphoma identifies distinct categories of the disease and is consistent with histogenetic derivation from germinal center-related B cells. Blood. 1998;92:1011–1019. - PubMed
-
- Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1937–1947. - PubMed
-
- Camilleri-Broet S, Criniere E, Broet P, et al. A uniform activated B-cell-like immunophenotype might explain the poor prognosis of primary central nervous system lymphomas: analysis of 83 cases. Blood. 2006;107:190–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

