K restriction inhibits protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B) and suppression of PP2B decreases ROMK channel activity in the CCD
- PMID: 18184875
- PMCID: PMC2734475
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00528.2007
K restriction inhibits protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B) and suppression of PP2B decreases ROMK channel activity in the CCD
Abstract
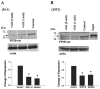
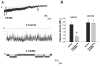
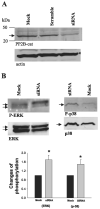
We used Western blot analysis to examine the effect of dietary K intake on the expression of serine/threonine protein phosphatase in the kidney. K restriction significantly decreased the expression of catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase (PP)2B but increased the expression of PP2B regulatory subunit in both rat and mouse kidney. However, K depletion did not affect the expression of PP1 and PP2A. Treatment of M-1 cells, mouse cortical collecting duct (CCD) cells, or 293T cells with glucose oxidase (GO), which generates superoxide anions through glucose metabolism, mimicked the effect of K restriction on PP2B expression and significantly decreased expression of PP2B catalytic subunits. However, GO treatment increased expression of regulatory subunit of PP2B and had no effect on expression of PP1, PP2A, and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1D. Moreover, deletion of gp91-containing NADPH oxidase abolished the effect of K depletion on PP2B. Thus superoxide anions or related products may mediate the inhibitory effect of K restriction on the expression of PP2B catalytic subunit. We also used patch-clamp technique to study the effect of inhibiting PP2B on renal outer medullary K (ROMK) channels in the CCD. Application of cyclosporin A or FK506, inhibitors of PP2B, significantly decreased ROMK channels, and the effect of PP2B inhibitors was abolished by blocking p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and ERK. Furthermore, Western blot demonstrated that inhibition of PP2B with cyclosporin A or small interfering RNA increased the phosphorylation of ERK and p38 MAPK. We conclude that K restriction suppresses the expression of PP2B catalytic subunits and that inhibition of PP2B decreases ROMK channel activity through stimulation of MAPK in the CCD.
Figures





References
-
- Adu D, Turney J, Michael J, McMaster P. Hyperkalaemia in cyclosporin-treated renal allograft recipients. Lancet. 1983;2:370–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

