Dynamics of neutrophil infiltration during cutaneous wound healing and infection using fluorescence imaging
- PMID: 18185533
- PMCID: PMC2617712
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701223
Dynamics of neutrophil infiltration during cutaneous wound healing and infection using fluorescence imaging
Abstract
Neutrophil influx is an early inflammatory response that is essential for the clearance of bacteria and cellular debris during cutaneous wounding. A non-invasive real-time fluorescence imaging technique was developed to examine the kinetics of enhanced green fluorescence protein-polymorphonuclear leukocyte (EGFP-PMN) influx within a wound. We hypothesized that infection or systemic availability would directly regulate the dynamics of EGFP-PMN recruitment and the efficiency of wound closure. Neutrophil recruitment increased dramatically over the first 24 hours from 10(6) at 4 hours up to a maximum of 5 x 10(6) EGFP-PMNs at 18 hours. A high rate of EGFP-PMN turnover was evidenced by approximately 80% decrease in EGFP signal within 6 hours. In response to wound colonization by Staphylococcus aureus or injection of GM-CSF, systemic PMNs increased twofold above saline control. This correlated with an increase in EGFP-PMN recruitment up to approximately 10(7) within the wound. Despite this effect by these distinct inflammatory drivers, wound closure occurred at a rate similar to the saline-treated control group. In summary, a non-invasive fluorescence-based imaging approach combined with genetic labeling of neutrophils provides a dynamic inner view of inflammation and the kinetics of neutrophil infiltration into the wounded skin over extended durations.
Figures
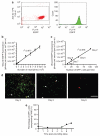
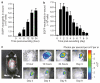
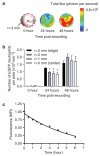
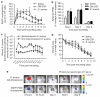
References
-
- Baskaran H, Yarmush ML, Berthiaume F. Dynamics of tissue neutrophil sequestration after cutaneous burns in rats. J Surg Res. 2000;93:88–96. - PubMed
-
- Cianfarani F, Tommasi R, Failla CM, Viviano MT, Annessi G, Papi M, et al. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor treatment of human chronic ulcers promotes angiogenesis associated with de novo vascular endothelial growth factor transcription in the ulcer bed. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:34–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

