Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: molecular mechanisms
- PMID: 18185852
- PMCID: PMC2180401
Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: molecular mechanisms
Abstract
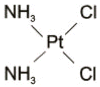
Cisplatin is one of the most widely used chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of several human malignancies. The efficacy of cisplatin is dose dependent, but the significant risk of nephrotoxicity frequently hinders the use of higher doses to maximize its antineoplastic effects. Several advances in our understanding of the biochemical and molecular mechanisms underlying cisplatin nephrotoxicity have recently emerged, and are reviewed in this article. Evidence is presented for distinct mechanisms of cisplatin toxicity in actively dividing tumor cells versus the normally quiescent renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. The unexpected role of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in cisplatin nephrotoxicity is elucidated. Recent studies demonstrating the ability of proximal tubular cells to metabolize cisplatin to a nephrotoxin are reviewed. The evidence for apoptosis as a major mechanism underlying cisplatin-induced renal cell injury is presented, along with the data exploring the role of specific intracellular pathways that may mediate the programmed cell death. The information gleaned from this review may provide critical clues to novel therapeutic interventions aimed at minimizing cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity while enhancing its antineoplastic efficacy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ergothioneine mitigates cisplatin-evoked nephrotoxicity via targeting Nrf2, NF-κB, and apoptotic signaling and inhibiting γ-glutamyl transpeptidase.Life Sci. 2021 Aug 1;278:119572. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119572. Epub 2021 May 6. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33964294
-
Hydrogen sulfide: A novel nephroprotectant against cisplatin-induced renal toxicity.Nitric Oxide. 2016 Jul 1;57:15-20. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Nitric Oxide. 2016. PMID: 27095538 Review.
-
Inhibition of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase or cysteine S-conjugate beta-lyase activity blocks the nephrotoxicity of cisplatin in mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Jan;300(1):142-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.300.1.142. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002. PMID: 11752109 Free PMC article.
-
The underlying mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and its therapeutic intervention using natural compounds.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;396(11):2925-2941. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02559-6. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37289283 Review.
-
3-deazaneplanocin A protects against cisplatin-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis and acute kidney injury by restoration of E-cadherin expression.Cell Death Dis. 2019 May 1;10(5):355. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1589-y. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31043583 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chemotherapy-Induced Central Retinal Artery Occlusion in Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia: Case Report.Int Med Case Rep J. 2020 Sep 15;13:431-435. doi: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S266456. eCollection 2020. Int Med Case Rep J. 2020. PMID: 32982483 Free PMC article.
-
Inauhzin sensitizes p53-dependent cytotoxicity and tumor suppression of chemotherapeutic agents.Neoplasia. 2013 May;15(5):523-34. doi: 10.1593/neo.13142. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 23633924 Free PMC article.
-
The physical and chemical stability of cisplatin (Teva) in concentrate and diluted in sodium chloride 0.9%.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2012;16(5):435-9. doi: 10.5114/wo.2012.31775. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2012. PMID: 23788924 Free PMC article.
-
Extremely low-frequency magnetic field enhances the therapeutic efficacy of low-dose cisplatin in the treatment of Ehrlich carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:189352. doi: 10.1155/2013/189352. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23484088 Free PMC article.
-
One stone, many birds: Recent advances in functional nanogels for cancer nanotheranostics.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022 Jul;14(4):e1791. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1791. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35338603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams JM, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell death. Science. 1996;281:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Anders MW. Mitochondrial bioactivation of cysteine S-conjugates and 4-thiaalkanoates: implications for mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1271:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Anders MW, Dekant W. Glutathione-dependent bioactivation of haloalkenes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1998;38:501–537. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1996;281:1305–1308. - PubMed
-
- Baliga R, Ueda N, Walker PD, Shah SV. Oxidant mechanisms in toxic acute renal failure. Am J Kid Dis. 1997;29:467–477. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
