CD47 associates with alpha 5 integrin and regulates responses of human articular chondrocytes to mechanical stimulation in an in vitro model
- PMID: 18186923
- PMCID: PMC2374443
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2350
CD47 associates with alpha 5 integrin and regulates responses of human articular chondrocytes to mechanical stimulation in an in vitro model
Abstract
Background: Recent studies provide evidence of roles for integrins in mechanical signalling in bone and cartilage. Integrin signalling is modulated by various mechanisms, including interaction with other transmembrane proteins. We aimed to identify whether one such protein, integrin-associated protein (CD47/IAP), is expressed by chondrocytes and whether it may regulate integrin-dependent mechanotransduction.
Methods: Chondrocytes, isolated from macroscopically normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage of human knee joints, were studied in a resting state or following mechanical stimulation at 0.33 Hz. CD47/IAP expression and associations were confirmed by immunohistology, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting, and immunoprecipitation. Roles in mechanotransduction were studied by assessing effects of function-blocking antibodies on a range of electrophysiological, cellular, and molecular responses of primary chondrocytes and responses of CD47/IAP-null cell lines transfected with CD47/IAP.
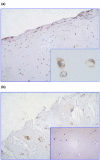
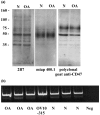
Results: Human articular chondrocytes were shown to express CD47/IAP, predominantly the type 2 isoform. Immunoprecipitation showed association of CD47/IAP with alpha5 integrin and thrombospondin but not SIRPalpha (signal-regulatory protein-alpha). The function-blocking anti-CD47/IAP antibody Bric 126 inhibited changes in membrane potential, tyrosine phosphorylation, and elevation of relative levels of aggrecan mRNA induced by mechanical stimulation, whereas in the presence of B6H12, an antibody that has partial agonist activity, a membrane depolarisation rather than a membrane hyperpolarisation response was induced by mechanical stimulation. CD47-null cell lines did not show changes in cell membrane potential following mechanical stimulation. Changes in cell membrane potential following mechanical stimulation were seen when CD47-null cells were transfected with CD47/IAP expression vectors but were not seen following mechanical stimulation of cells transfected with vectors for the extracellular immunoglobulin variable (IgV) domain of CD47/IAP in the absence of the transmembrane and intracellular domains.
Conclusion: CD47/IAP is necessary for chondrocyte mechanotransduction. Through interactions with alpha5beta1 integrin and thrombospondin, CD47/IAP may modulate chondrocyte responses to mechanical signals.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in human articular chondrocytes.Biorheology. 2006;43(3,4):223-33. Biorheology. 2006. PMID: 16912396
-
Mechanical responses and integrin associated protein expression by human ankle chondrocytes.Biorheology. 2006;43(3,4):249-58. Biorheology. 2006. PMID: 16912398
-
Mechanical regulation of proteoglycan synthesis in normal and osteoarthritic human articular chondrocytes--roles for alpha5 and alphaVbeta5 integrins.Biorheology. 2008;45(3-4):275-88. Biorheology. 2008. PMID: 18836230
-
Integrin-interleukin-4 mechanotransduction pathways in human chondrocytes.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001 Oct;(391 Suppl):S49-60. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200110001-00006. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. PMID: 11603724 Review.
-
Integrin-dependent signal cascades in chondrocyte mechanotransduction.Ann Biomed Eng. 2004 Mar;32(3):435-46. doi: 10.1023/b:abme.0000017538.72511.48. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004. PMID: 15095818 Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquilin-2 (UBQLN2) binds with high affinity to the C-terminal region of TDP-43 and modulates TDP-43 levels in H4 cells: characterization of inhibition by nucleic acids and 4-aminoquinolines.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1834(6):964-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.03.020. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23541532 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoscale imaging of CD47 informs how plasma membrane modifications shape apoptotic cell recognition.Commun Biol. 2023 Feb 22;6(1):207. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04558-y. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 36813842 Free PMC article.
-
Role of integrins and their ligands in osteoarthritic cartilage.Rheumatol Int. 2015 May;35(5):787-98. doi: 10.1007/s00296-014-3137-5. Epub 2014 Sep 27. Rheumatol Int. 2015. PMID: 25261047 Review.
-
Cell adhesion receptors in mechanotransduction.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Oct;20(5):551-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.05.005. Epub 2008 Jun 24. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18583124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrins and chondrocyte-matrix interactions in articular cartilage.Matrix Biol. 2014 Oct;39:11-6. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Aug 25. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 25169886 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meachim G. The Aetiopathogenesis of Osteoarthrosis. London, Pitman Medical; 1980.
-
- Millward-Sadler SJ, Wright MO, Davies LW, Nuki G, Salter DM. Mechanotransduction via integrins and interleukin-4 results in altered aggrecan and matrix metalloproteinase 3 gene expression in normal, but not osteoarthritic, human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2091–2099. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9<2091::AID-ANR21>3.0.CO;2-C. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wright MO, Nishida K, Bavington C, Godolphin JL, Dunne E, Walmsley S, Jobanputra P, Nuki G, Salter DM. Hyperpolarisation of cultured human chondrocytes following cyclical pressure-induced strain: evidence of a role for alpha 5 beta 1 integrin as a chondrocyte mechanoreceptor. J Orthop Res. 1997;15:742–747. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100150517. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

