Biomarkers to predict recurrent cardiovascular disease: the Heart and Soul Study
- PMID: 18187073
- PMCID: PMC2239343
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.06.030
Biomarkers to predict recurrent cardiovascular disease: the Heart and Soul Study
Abstract
Purpose: The study purpose was to evaluate the ability of 6 biomarkers to improve the prediction of cardiovascular events among persons with established coronary artery disease.
Background: Cardiovascular risk algorithms are designed to predict the initial onset of coronary artery disease but are less effective in persons with preexisting coronary artery disease.
Methods: We examined the association of N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (Nt-proBNP), cystatin C, albuminuria, C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6, and fibrinogen with cardiovascular events in 979 Heart and Soul Study participants with coronary artery disease after adjusting for demographic, lifestyle, and behavior variables; cardiovascular risk factors; cardiovascular disease severity; medication use; and left ventricular ejection fraction. The outcome was a composite of stroke, myocardial infarction, and coronary heart disease death during an average of 3.5 years of follow-up.
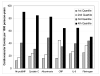
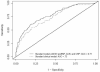
Results: During follow-up, 142 participants (15%) developed cardiovascular events. The highest quartiles (vs lower 3 quartiles) of 5 biomarkers were individually associated with cardiovascular risk after multivariate analysis: Nt-proBNP hazard ratio (HR)=2.13 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.43-3.18); cystatin C HR=1.72 (95% CI, 1.10-2.70); albuminuria HR=1.71 (95% CI, 1.15-2.54); CRP HR=2.00 (95% CI, 1.40-2.85); and interleukin-6 HR=1.76 (95% CI, 1.22-2.53). When all biomarkers were included in the multivariable analysis, only Nt-proBNP, albuminuria, and CRP remained significant predictors of events: HR=1.88 (95% CI, 1.23-2.85), HR=1.63 (95% CI, 1.09-2.43), and HR=1.82 (95% CI, 1.24-2.67), respectively. The area under the receiver operator curve for clinical predictors alone was 0.73 (95% CI, 0.68-0.78); adding Nt-proBNP, albuminuria, and CRP significantly increased the area under the receiver operator curve to 0.77 (95% CI, 0.73-0.82, P<.005).
Conclusion: Among persons with prevalent coronary artery disease, biomarkers reflecting hemodynamic stress, kidney damage, and inflammation added significant risk discrimination for cardiovascular events.
Figures
References
-
- Sabatine MS, Morrow DA, de Lemos JA, et al. Multimarker approach to risk stratification in non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes: simultaneous assessment of troponin I, C-reactive protein, and B-type natriuretic peptide. Circulation. 2002 Apr 16;105(15):1760–1763. - PubMed
-
- Vittinghoff E, Shlipak MG, Varosy PD, et al. Risk factors and secondary prevention in women with heart disease: the Heart and Estrogen/progestin Replacement Study. Ann Intern Med. 2003 Jan 21;138(2):81–89. - PubMed
-
- Erlandsen EJ, Randers E, Kristensen JH. Evaluation of the Dade Behring N Latex Cystatin C assay on the Dade Behring Nephelometer II System. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1999 Feb;59(1):1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

