The elmiric acids: biologically active anandamide analogs
- PMID: 18187165
- PMCID: PMC2621443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.11.011
The elmiric acids: biologically active anandamide analogs
Abstract
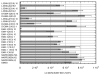
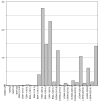
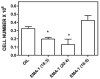
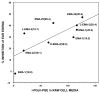
As chemical entities, lipoamino acids have been known for some time. However, more recently their occurrence and importance in mammalian species has been discovered. They appear to have close relationships with the endocannabinoids not only structurally but also in terms of biological actions. The latter include analgesia, anti-inflammatory effects, inhibition of cell proliferation and calcium ion mobilization. To date about 40 naturally occurring members of this family have been identified and, additionally, several synthetic analogs have been prepared and studied. To facilitate their identity, a nomenclature system has been suggested based on the name elmiric acid (EMA). The prototypic example, N-arachidonoyl glycine, does not bind to CB1, however it does inhibit the glycine transporter GLYT2a and also appears to be a ligand for the orphan G-protein-coupled receptor GPR18. It may also have a role in regulating tissue levels of anandamide by virtue of its inhibitory effect on FAAH the enzyme that mediates inactivation of anandamide. Its concentration in rat brain is several-fold higher than anandamide supporting its possible role as a physiological mediator. Future studies should be aimed at elucidating the actions of all of the members of this interesting family of molecules.
Figures

References
-
- Batrakov SG, Mosezhnyi AE, Ruzhitsky AO, Sheichenko VI, Nikitin DI. The polar-lipid composition of the sphingolipid-producing bacterium Flectobacillus major. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1484:225–240. - PubMed
-
- Bradshaw HB, Rimmerman N, Krey JF, Walker JM. Sex and hormonal cycle differences in rat brain levels of pain-related cannabimimetic lipid mediators. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006;291:R349–358. - PubMed
-
- Bradshaw HB, Hu SS, Rimmerman N, O'Dell DK, Cravatt BF, Walker JM. Novel metabolism of N-arachidonoyl glycine by fatty acid amide hydrolase. Neurosci abs 2006
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

