Synthesis of and evaluation of lipid A modification by 4-substituted 4-deoxy arabinose analogs as potential inhibitors of bacterial polymyxin resistance
- PMID: 18187325
- PMCID: PMC2516481
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.12.061
Synthesis of and evaluation of lipid A modification by 4-substituted 4-deoxy arabinose analogs as potential inhibitors of bacterial polymyxin resistance
Abstract
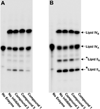
Three sets of novel 4-deoxy-l-arabinose analogs were synthesized and evaluated as potential inhibitors of the bacterial resistance mechanism in which lipid A, on the outer membrane, is modified with 4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose (l-Ara4N). One compound diminished the transfer of l-Ara4N onto lipid A. These results suggest that small molecules might be designed that would effect the same reversal of bacterial resistance observed in genetic knockouts.
Figures




References
-
- Beringer P. The clinical use of colistin in patients with cystic fibrosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2001;7(6):434–440. - PubMed
-
- Brogden KA. Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3(3):238–250. - PubMed
-
- Peschel A. How do bacteria resist human antimicrobial peptides? Trends Microbiol. 2002;10(4):179–186. - PubMed
-
- McPhee JB, Lewenza S, Hancock RE. Cationic antimicrobial peptides activate a two-component regulatory system, PmrA-PmrB, that regulates resistance to polymyxin B and cationic antimicrobial peptides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol. 2003;50(1):205–217. - PubMed
-
- Bader MW, Navarre WW, Shiau W, Nikaido H, Frye JG, McClelland M, Fang FC, Miller SI. Regulation of Salmonella typhimurium virulence gene expression by cationic antimicrobial peptides. Mol Microbiol. 2003;50(1):219–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

