A balance between NF-Y and p53 governs the pro- and anti-apoptotic transcriptional response
- PMID: 18187512
- PMCID: PMC2275158
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm1046
A balance between NF-Y and p53 governs the pro- and anti-apoptotic transcriptional response
Abstract
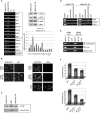
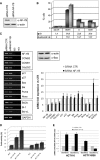
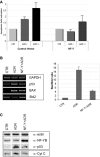
The transcription factor NF-Y is a trimer with histone-like subunits that binds and activates CCAAT-containing promoters. NF-Y controls the expression of several key regulators of the cell cycle. In this study, we examined the functional and molecular effects of NF-YB knockdown. Cell cycle progression is affected with a G2/M-specific depletion. This is due to the inability of activation of G2/M-specific genes, as evidenced by expression profiling, RT-PCR and ChIP data. Surprisingly, apoptosis is also observed, with Caspase 3/7/8 cleavage. A role of p53 and Bcl-2 family members is important. NF-YB inactivation is sufficient to functionally activate p53, in the absence of DNA damage. Failure to maintain a physiologic level of CCAAT-dependent transcription of anti-apoptotic genes contributes to impairment of Bax/Bcl-2 and Bax/Bcl-X(L) ratios. Our data highlight the importance of fine balancing the NF-Y-p53 duo for cell survival by (i) maintaining transcription of anti-apoptotic genes and (ii) preventing p53 activation that triggers the apoptotic cascade.
Figures
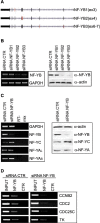
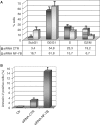

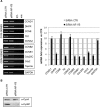
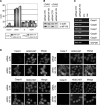
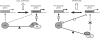
References
-
- Bucher P. Weight matrix descriptions of four eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoter elements derived from 502 unrelated promoter sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;212:563–578. - PubMed
-
- Maity SN, de Crombrugghe B. Role of the CCAAT-binding protein CBF/NF-Y in transcription. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998;23:174–178. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani R. The molecular biology of the CCAAT-binding factor NF-Y. Gene. 1999;239:15–27. - PubMed
-
- McNabb DS, Xing Y, Guarente L. Cloning of yeast HAP5: a novel subunit of a heterotrimeric complex required for CCAAT binding. Genes Dev. 1995;9:47–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

