Mitogen-activated protein kinase contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of corticotropin-releasing hormone synthesizing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus
- PMID: 18187539
- PMCID: PMC2329264
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2007-1478
Mitogen-activated protein kinase contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of corticotropin-releasing hormone synthesizing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus
Abstract
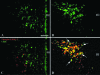
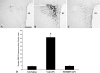
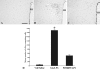
To determine whether the p44/p42 MAPK (ERK1/2) signaling pathway is involved in the activation of CRH-containing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) after bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration, Sprague Dawley rats were injected with LPS, and studied after 2, 6, 9, and 12 h. In saline-treated controls, isolated weak phosphorylated (phospho)ERK1/2 immunoreactive neurons were observed in the PVN. However, a dramatic increase in phospho-ERK1/2 immunoreactivity was apparent in the PVN 2 h after LPS administration, and gradually declined to baseline levels 9-12 h after injection. By double-labeling immunofluorescence, all CRH-containing neurons in the PVN contained phospho-ERK1/2 2 h after LPS. Intracerebroventricular administration of the MAPK inhibitor, PD98059, prevented LPS-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation, c-fos activation, and the increase of CRH gene expression in the PVN but had no effect on c-fos activation in brainstem A2-C1/C2 regions. We conclude that LPS rapidly increases the phospho-ERK1/2 in CRH-containing neurons in the PVN and that activation of MAPKs is necessary for LPS-induced activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identifying links in the chain: the dynamic coupling of catecholamines, peptide synthesis, and peptide release in hypothalamic neuroendocrine neurons.Adv Pharmacol. 2013;68:421-44. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-411512-5.00020-8. Adv Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24054156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central LPS-induced c-fos expression in the PVN and the A1/A2 brainstem noradrenergic cell groups is altered by adrenalectomy.Neuroendocrinology. 1999 Sep;70(3):175-85. doi: 10.1159/000054474. Neuroendocrinology. 1999. PMID: 10516480
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical responses to single vs. repeated endotoxin lipopolysaccharide administration in the rat.Brain Res. 1997 Sep 5;767(2):181-91. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(97)00460-5. Brain Res. 1997. PMID: 9367246
-
Central administration of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript increases phosphorylation of cAMP response element binding protein in corticotropin-releasing hormone-producing neurons but not in prothyrotropin-releasing hormone-producing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus.Brain Res. 2004 Mar 5;999(2):181-92. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2003.11.062. Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 14759497
-
Stress Adaptation and the Brainstem with Focus on Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 23;22(16):9090. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169090. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445795 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying links in the chain: the dynamic coupling of catecholamines, peptide synthesis, and peptide release in hypothalamic neuroendocrine neurons.Adv Pharmacol. 2013;68:421-44. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-411512-5.00020-8. Adv Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24054156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress-induced glucocorticoid desensitizes adrenoreceptors to gate the neuroendocrine response to somatic stress in male mice.Cell Rep. 2022 Oct 18;41(3):111509. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111509. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36261014 Free PMC article.
-
Light-induced rapid Ca²⁺ response and MAPK phosphorylation in the cells heterologously expressing human OPN5.Sci Rep. 2014 Jun 19;4:5352. doi: 10.1038/srep05352. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24941910 Free PMC article.
-
The day/night difference in the circadian clock's response to acute lipopolysaccharide and the rhythmic Stat3 expression in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 28;13(9):e0199405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199405. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30265676 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical protein kinase C activity in the hypothalamus is required for lipopolysaccharide-mediated sickness responses.Endocrinology. 2009 Dec;150(12):5362-72. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0509. Epub 2009 Oct 9. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19819945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akil HCS, Cullinan WE, Lechan RM, Toni R, Watson SJ, Moore RY 1999 Neuroendocrine systems I: overview-thyroid and adrenal axes. In: Fundamental neuroscience. Zigmond H, Bloom F, Landis S, Roberts J, Squire L, eds. San Diego: Academic Press; 1127–1150
-
- Whitnall MH 1989 Stress selectively activates the vasopressin-containing subset of corticotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Neuroendocrinology 50:702–707 - PubMed
-
- Whitnall MH 1993 Regulation of the hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone neurosecretory system. Prog Neurobiol 40:573–629 - PubMed
-
- Beishuizen A, Thijs LG 2003 Endotoxin and the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. J Endotoxin Res 9:3–24 - PubMed
-
- Khan AM, Watts AG 2004 Intravenous 2-deoxy-D-glucose injection rapidly elevates levels of the phosphorylated forms of p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinases (extracellularly regulated kinases 1/2) in rat hypothalamic parvicellular paraventricular neurons. Endocrinology 145:351–359 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

