Nitric oxide isoenzymes regulate lipopolysaccharide-enhanced insulin transport across the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 18187549
- PMCID: PMC2276709
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2007-1091
Nitric oxide isoenzymes regulate lipopolysaccharide-enhanced insulin transport across the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
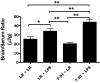
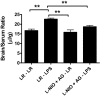
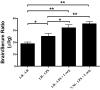
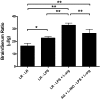
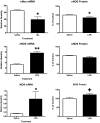
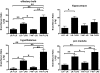
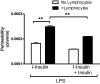
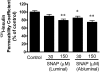
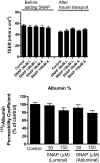
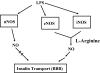
Insulin transported across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) has many effects within the central nervous system. Insulin transport is not static but altered by obesity and inflammation. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), derived from the cell walls of Gram-negative bacteria, enhances insulin transport across the BBB but also releases nitric oxide (NO), which opposes LPS-enhanced insulin transport. Here we determined the role of NO synthase (NOS) in mediating the effects of LPS on insulin BBB transport. The activity of all three NOS isoenzymes was stimulated in vivo by LPS. Endothelial NOS and inducible NOS together mediated the LPS-enhanced transport of insulin, whereas neuronal NOS (nNOS) opposed LPS-enhanced insulin transport. This dual pattern of NOS action was found in most brain regions with the exception of the striatum, which did not respond to LPS, and the parietal cortex, hippocampus, and pons medulla, which did not respond to nNOS inhibition. In vitro studies of a brain endothelial cell (BEC) monolayer BBB model showed that LPS did not directly affect insulin transport, whereas NO inhibited insulin transport. This suggests that the stimulatory effect of LPS and NOS on insulin transport is mediated through cells of the neurovascular unit other than BECs. Protein and mRNA levels of the isoenzymes indicated that the effects of LPS are mainly posttranslational. In conclusion, LPS affects insulin transport across the BBB by modulating NOS isoenzyme activity. NO released by endothelial NOS and inducible NOS acts indirectly to stimulate insulin transport, whereas NO released by nNOS acts directly on BECs to inhibit insulin transport.
Figures
References
-
- Blasberg RG, Fenstermacher JD, Patlak CS 1983 Transport of α-aminoisobutyric acid across brain capillary and cellular membranes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3:8–32 - PubMed
-
- Henneberg N, Hoyer S 1994 Short-term or long-term intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) infusion of insulin exhibits a discrete anabolic effect on cerebral energy metabolism in the rat. Neurosci Lett 175:153–156 - PubMed
-
- Hoyer S 2003 Memory function and brain glucose metabolism. Pharmacopsychiatry 36:S62–S67 - PubMed
-
- Kwok RP, Juorio AV 1988 Effects of insulin on rat brain noradrenaline. Neurochem Res 13:887–892 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

