CD47: a new target in cardiovascular therapy
- PMID: 18187671
- PMCID: PMC2553319
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.158154
CD47: a new target in cardiovascular therapy
Abstract
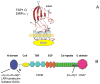
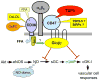
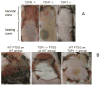
CD47, originally named integrin-associated protein, is a receptor for thrombospondin-1. A number of important roles for CD47 have been defined in regulating the migration, proliferation, and survival of vascular cells, and in regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. The recent discovery that thrombospondin-1 acts via CD47 to inhibit nitric oxide signaling throughout the vascular system has given new importance and perhaps a unifying mechanism of action to these enigmatic proteins. Here we trace the development of this exciting new paradigm for CD47 function in vascular physiology.
Figures
References
-
- Reinhold MI, Lindberg FP, Plas D, Reynolds S, Peters MG, Brown EJ. In vivo expression of alternatively spliced forms of integrin associated protein (CD47) J Cell Sci. 1995;108:3419–3425. - PubMed
-
- Lindberg FP, Lublin DM, Telen MJ, Veile RA, Miller YE, Donis-Keller H, Brown EJ. Rh-related antigen CD47 is the signal-transducer integrin associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:1567–1570. - PubMed
-
- Gao A-GFP, Lindberg MB, Finn SD, Blystone EJ, Brown Frazier WA. Integrin-associated protein is a receptor for the C-terminal domain of thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1996b;271:21–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

